Managing absence templates
In this guide:
- HR documents and templates
- Recruitment forms and templates
- Job offers, inductions and new starts templates
- Time off work policies and procedures
- Maternity, paternity, adoption, parental and shared parental leave letters and forms
- Managing absence templates
- Performance management and staff training templates
- Grievance and disciplinary procedures and templates
- Redundancy letters, forms and templates
- Other key HR policies and templates
Recruitment forms and templates
Sample recruitment templates including forms, letters, and documents to help you recruit, shortlist and interview potential employees.
Recruitment and selection of new employees should always be considered carefully by any business regardless of their size. The people you employ will form an essential part of your business strategy and will contribute greatly to the success of your business.
Staff recruitment templates
To ensure you attract the best people, you will need to ensure that your recruitment process is fine-tuned, non-discriminatory, and tailored to your business needs. For further guidance see the Employer's Handbook Section 2: Recruiting new employees (PDF, 420K).
For an overview of the recruitment stages and general considerations, download our recruitment process flowchart (DOC, 87K).
For sample template recruitment documents to help with particular stages of the recruitment process, see below.
Templates for advertising your job vacancy
You will need to prepare a job description, a personnel specification, and an application form to advertise your job vacancy. To help you do this, you can download and use our sample template recruitment documents and forms:
- sample job description template (DOC, 14K)
- sample personnel specification template (DOC, 15K)
- sample recruitment advertisement template (DOC, 16K)
- sample job application form template (DOC, 18K)
- sample monitoring questionnaire for job applicants template (DOC, 20K)
Templates for shortlisting candidates
Once you receive replies from candidates to your job vacancy advertisement, you will need to draw up a shortlist and invite those shortlisted to an interview. To help you do this, you can download and use our sample shortlisting documentation templates:
- sample shortlisting record table template (DOC, 15K)
- shortlisting guidance (DOC, 13K)
- sample letter of invitation to first interview template (DOC, 13K)
- sample rejection letter to applicant following shortlisting exercise template (DOC, 13K)
Templates for interviewing candidates
The more preparation you do for the job interview, the easier it will be for both you and the candidate. To help you prepare and carry out the interview process correctly, download and read our factsheets on interviewing, and use our sample record of interview templates:
- sample interview record document template (DOC, 14K)
- sample interview report document template (DOC, 14K)
- preparing for job interviews factsheet (DOC, 14K)
- interview practicalities and structure (DOC, 14K)
- do's and don'ts of interviewing job applicants (DOC, 15K)
- sample rejection letter to applicant following job interview template (DOC, 12K)
Read more on advertising a job and interviewing candidates.
Recruitment and selection tutorial videos
The embedded video below is an introduction to a tutorial on recruitment and selection. You can view the full Invest NI recruitment & selection tutorial.
ActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/recruitment-forms-and-templates
Links
Job offers, inductions and new starts templates
Use our sample job offer letters, induction plans, and contract of employment to welcome and start a new member of your staff.
The final stage of the recruitment process involves choosing the successful candidate and making them a job offer.
You will need to consider whether you wish to make a job offer that is conditional on satisfactory references and right to work checks. If your job offer is accepted, you should arrange an induction plan for your new starter and consider the terms of your contract of employment.
Specific Employers' Handbook guidance
For further guidance on job offers, inductions and employment contracts see the following sections of the Invest Northern Ireland Employer's Handbook:
For sample documents to help you conclude your recruitment exercise fairly and efficiently, see relevant sections below.
Job offers
The initial job offer may be made by telephone. This should help you quickly establish if the individual wants to accept the job you are offering.
If that is the case, you should follow up with a formal letter of offer, and include details of any conditions attached to the job offer, eg satisfactory references. To help you do this, you can download and use our sample job offer letter and reference check form:
- sample letter of job offer to successful candidate (DOC, 12K)
- sample reference check form (DOC, 12K)
Contract of employment
The moment a candidate unconditionally accepts your offer of a job, a contract of employment comes into existence. To help you draft a contract of employment suitable to your business needs and the role in question, download and use our sample contract of employment, as well as staff policy documents to be included in it:
- sample contract of employment (DOC, 46K)
- sample sickness/absence notification and pay procedure (DOC, 27K)
Even if you do not issue a written contract of employment, you are under a legal duty to provide most employees with a written statement of main employment particulars within two months of the start of their employment with you.
Induction
You should aim to introduce, familiarise and integrate your new employee into your business as quickly as possible. Early induction will not only provide new-starters with the information they need to settle in, but will also provide them with the knowledge and skills that will help them contribute to your business right from the start.
To help you devise your staff induction activities, download and use our sample induction plans:
See induction programme: what to include.
View all recruitment & Selection - Invest NI tutorial videos.
ActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/job-offers-inductions-and-new-starts-templates
Links
Time off work policies and procedures
Download a sample working time opt-out agreement and steps to help you determine your workers' leave entitlement.
You should set your normal working hours in your employment contract, or written statement of employment. Unless you operate within certain sectors, you cannot force your workers to work for more than 48 hours per week on average.
Special working time rules apply to young people. Find further information on hours, rest breaks and the working week.
If your workers wish to work for longer than 48 hours per week, they can choose to opt out of the Working Time Regulations. This must be done voluntarily and in writing in order for you to comply with the law.
Download our sample working time opt-out agreement (DOC, 14K).
Remember that you can't force your workers to sign an opt-out agreement or to cancel it, though a worker can cancel it voluntarily after giving you appropriate notice.
Annual leave
Most workers are legally entitled to paid holidays/annual leave.
A worker's statutory paid holiday entitlement in Northern Ireland is 5.6 weeks. This amounts to 28 days for a worker working a five-day week. This can include public and bank holidays. See:
- Know how much holiday to give your staff
- Calculate your employees' holiday entitlement
- Bank and public holiday dates
The leave entitlement for part-time workers or those who are about to leave employment is calculated on a pro-rata basis. Use the following step-by-step guidance to calculate how much leave these workers may be entitled to:
- download steps for determining leave entitlement of part-time workers (DOC, 13K)
- download steps for determining leave entitlement of leavers (DOC, 13K)
For additional leave information, such us notice periods, restrictions and holiday pay, see know how much holiday to give your staff.
For further guidance see Employers' Handbook Section 4: Working hours, rest breaks and time off (PDF, 83K).
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/time-work-policies-and-procedures
Links
Maternity, paternity, adoption, parental and shared parental leave letters and forms
Sample letters and application forms to help you manage your workers' rights to maternity, paternity, adoption, and shared parental leave.
Your responsibilities in relation to rights of working parents - or parents to be - are explained in our maternity, paternity, adoption and parental leave section.
Specific Employers' Handbook guidance
Further best practice advice and practical documents to help you communicate with your workers in respect of their entitlements are included in the Invest Northern Ireland Employers' Handbook including:
- Section 8: Maternity leave and pay (PDF, 83K)
- Section 9: Paternity leave and pay (PDF, 71K)
- Section 10: Adoption leave and pay (PDF, 71K)
- Section 11: Shared parental leave and pay (PDF, 114K)
- Section 12: Parental leave, parental bereavement leave and time off for dependants (PDF, 82K)
Sample employer documents
You can download, customise and use sample documents from the handbook that are relevant to maternity, paternity, adoption, parental and shared parental leave:
- model letter for employers to acknowledge notification of maternity leave (DOC, 14K)
- model letter for employers to acknowledge notification of adoption leave (DOC, 14K)
- sample employee application for parental leave (DOC, 14K)
- sample letter to employee of notification of postponement of parental leave (DOC, 13K)
- sample shared parental leave (birth) policy (DOC, 39K)
- sample shared parental leave (adoption) policy (DOC, 38K)
- sample confirmation of entitlement to shared parental leave (DOC, 27K)
- sample confirmation of shared parental leave booking (DOC, 27K)
- sample shared parental leave request to discuss leave booking (DOC, 27K)
- sample shared parental leave refusal of a discontinuous leave booking (DOC, 27K)
For help with administering paternity and adoption leave, use the maternity, paternity and adoption leave and pay calculator for employers.
ActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/maternity-paternity-adoption-parental-and-shared-parental-leave-letters-and-forms
Links
Managing absence templates
Sample documents to help you manage staff absence with employment policies that follow good practice and comply with legislation.
Managing staff absence is a frequent and critical element to good people management within a business.
Absence causes difficulties both for the person who is absent and for the organisation. For small organisations in particular, where there are limited resources to cover and cope with the direct and indirect costs of an absence, it can be very disruptive.
Manage absence guidance
Further best practice advice and guidance to help your manage staff absence is included in the Invest Northern Ireland Employers' Handbook Section 19: Managing absence (PDF, 154K).
Manage absence templates
Sample templates are included in this section on managing staff absence that you can download and adapt specifically for your business purposes including:
- return to work interview format (DOC, 13K)
- example letter to employee seeking consent for a medical report from employee's GP (DOC, 14K)
- consent form for access to medical reports (DOC, 13K)
- summary of employee rights under the Access to Personal Files and Medical Reports (NI) Order 1991 (DOC, 15K)
- request to employee's GP for medical assessment (DOC, 15K)
- sample letter to an occupational health doctor requesting opinion on fitness for work (DOC, 14K)
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/managing-absence-templates
Links
Performance management and staff training templates
Sample letters and application forms to help you train and develop your staff, and monitor their performance.
Improving the skills of your staff can deliver real business benefits. It can increase their productivity, motivation and quality of work, and boost overall business profits and customer satisfaction. We have a number of free performance management and staff training templates that employers and HR professionals can use for their business.
Employers' Handbook: staff performance and training
Further best practice advice and practical documents to help you with staff performance, training and development are included in the Invest Northern Ireland Employers' Handbook including:
- Section 14: Managing employee performance (PDF, 229K)
- Section 15: Training and development (PDF, 69K)
Performance management templates
Agreeing appropriate objectives and making effective use of appraisals can improve your business performance and help you assess how well your employees are working.
If you're not sure where to start setting performance targets, download our sample agreement templates for different positions within the business:
- general performance agreement template (DOC, 13K)
- sample performance agreement - for operatives (DOC, 13K)
- sample performance agreement - for administrators (DOC, 15K)
- sample performance agreement - for managers (DOC, 14K)
Performance reviews templates
Download our two sample performance review form templates to help you assess employees' performance:
- sample performance review form (DOC, 18K)
- sample performance review form past and future performance (DOC, 16K)
Dealing with poor performance
Performance improvement measures can help you manage poor performance, and deal with your staff efficiently and fairly.
To see an overview of the measures required to deal with poor performance, download our formal performance improvement procedure flowchart (DOC, 20K).
Poor performance template letters
Use our downloadable sample letters to help you follow a fair and efficient performance improvement procedure when dealing with underperforming staff:
- sample letter of notice of performance improvement meeting (DOC, 13K)
- sample letter of recorded verbal warning due to poor performance (DOC, 14K)
- sample letter of first written warning due to poor performance (DOC, 14K)
- sample letter of final written warning due to poor performance (DOC, 14K)
- sample letter of dismissal or disciplinary action due to poor performance (DOC, 14K)
- sample letter of outcome of appeal following disciplinary action due to poor performance (DOC, 14K)
Training and development templates
Creating a training strategy usually involves assessing your training needs, determining the type of training best suited to your business and evaluating its effects to maximise the benefits.
To help get you started on the way to creating a successful training strategy, you can download and use the following training and development templates:
For further information, see training your staff and managing staff performance.
Training needs analysis tutorial videos
The embedded video below is an introduction to a tutorial on training needs analysis. You can view the full Invest NI training needs analysis tutorial.
ActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/performance-management-and-staff-training-templates
Links
Grievance and disciplinary procedures and templates
Free templates to help employers and HR professionals handle any grievance, discipline, or dismissal situation fairly and in keeping with the law.
Even in well-run businesses, it may sometimes be necessary to deal with employee's grievances or disciplinary issues, or even dismissals. Having written rules and procedures for employee grievances or disciplinary issues may help you deal with them fairly and in keeping with employment law.
Specific Employers' Handbook guidance
Further best practice advice and practical templates to help you with staff grievances, disciplinary issues and dismissals are included in the Invest Northern Ireland Employers' Handbook including:
- Section 17: Employee grievances (PDF, 71K)
- Section 18: Disciplinary issues and dismissal (PDF, 143K)
For sample templates to help you deal with grievance, discipline, and dismissal situations, see the relevant sections below.
Grievance templates
Your grievance rules and procedures should be set out in writing and follow the good practice principles set out in the Labour Relations Agency (LRA) Code of Practice on Disciplinary and Grievance Procedures.
Download our sample letters and procedures templates to help you deal with grievances in your workplace:
- sample grievance procedure (DOC, 17K)
- sample letter of invitation to investigatory meeting - employee raising a grievance (DOC, 14K)
- sample letter of invitation to investigatory meeting - person against whom a grievance is raised (DOC, 14K)
Discipline and dismissal templates
Your disciplinary rules and procedures should be set out in writing and follow the good practice principles set out in the LRA Code of Practice on Disciplinary and Grievance Procedures.
Failure to meet this requirement may result in extra compensation for the employee if they succeed in a tribunal claim.
Download our sample notices and procedures templates to help you deal with disciplinary issues in your workplace:
- sample disciplinary rules and procedures for misconduct (DOC, 29K)
- sample notice of the disciplinary meeting (DOC, 14K)
- sample notice of the recorded disciplinary warning (DOC, 14K)
- sample notice of the appeal meeting against the disciplinary warning (DOC, 14K)
- sample notice of the result of the appeal against the disciplinary warning (DOC, 14K)
- sample notice of dismissal or disciplinary action to be taken (DOC, 12K)
- sample letter to be sent by the employer after the disciplinary meeting (DOC, 15K)
- sample notice of the appeal meeting against dismissal or disciplinary action (DOC, 14K)
- sample notice of the result of the appeal against the dismissal or disciplinary action (DOC, 14K)
- sample letter to be sent by the employer, setting out the reasons for the proposed dismissal or action other than dismissal and arranging the meeting (DOC, 15K)
For further information, see handling grievances, disciplinary procedures, hearings and appeals and dismissing employees.
ActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/grievance-and-disciplinary-procedures-and-templates
Links
Redundancy letters, forms and templates
Forms and templates to help employers manage the redundancy process including redundancy letter templates.
A redundancy situation can arise in the following circumstances:
- the employer has ceased, or intends to cease, to carry on the business for the purposes of which the employee was so employed
- the employer has ceased, or intends to cease, to carry on the business in the place where the employee was so employed
- the requirements of the business for employees to carry out work of a particular kind has ceased or diminished or are expected to cease or diminish
- the requirements of the business for the employees to carry out work of a particular kind, in the place where they were so employed, has ceased or diminished or are expected to cease or diminish
Employers' Handbook redundancy guidance
Further best practice advice and practical documents to help you with redundancy are included in the Invest Northern Ireland Employers' Handbook including Section 22: Redundancy procedure (PDF, 199K)
Sample redundancy letters and documents
You can download the sample redundancy templates below to help you manage the redundancy process:
- redundancy ready reckoner table (DOC, 1MB)
- sample redundancy selection matrix template (DOC, 17K)
- sample redundancy letter for provisional selection for redundancy (DOC, 14K)
- sample redundancy letter for invitation to final consultation (DOC, 14K)
- sample redundancy letter for confirmation of redundancy (DOC, 16K)
- sample letter of offer of alternative role (DOC, 14K)
- sample letter for result of appeal (DOC, 14K)
- advance notification of redundancies form template (DOC, 21K)
For further information, see redundancy, restructures and change.
Alternatives to redundancy
You may wish to consider alternatives in order to avoid redundancies. For further guidance see Section 23: Lay-off and short-time working (PDF, 58K) of the Invest Northern Ireland Employers' Handbook.
Redundancy webinar
The Labour Relations Agency (LRA) redundancy webinar provides useful information on the topic of redundancy and how to ensure the redundancy process is managed fairly and in line with employment legislation.
ActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/redundancy-letters-forms-and-templates
Links
Other key HR policies and templates
Sample documents to help you develop employment policies that follow good practices and comply with legislation.
You do not have to have a staff policy on every single aspect of your business. However, as an employer, you must legally set out details of your dismissal/disciplinary procedures in writing and, if you employ five or more people, you must have a written health and safety policy.
In instances where there may be no legal requirement, it is still good practice to set out formal written policies so that workers understand what is expected of them and what they can expect in return.
Other sample employer templates and documents
To help you develop up-to-date and compliant employer policies and procedures, you can download, customise and use our templates and sample documents:
- sample meeting action list (DOC, 13K)
- sample alcohol and drug policy (DOC, 17K)
- social media, internet and email policy and guidance checklist (DOC, 15K)
- sample social media, internet and email security policy guidelines (DOC, 24K)
Please note that this is not an exhaustive list of possible employment policies.
You should also consider developing policies on issues such as working time and time off, equality and diversity, bullying and harassment, training and performance management, and others.
To find more information on other relevant policies, see set up employment policies for your business.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/other-key-hr-policies-and-templates
Links
Developing a staff training plan - Grants Electrical Services (video)
In this guide:
- Staff training
- Advantages of staff training
- How to identify staff training needs
- Develop a staff training plan
- Training methods to fit your business
- Find training courses in Northern Ireland
- Skill Up programme: Retrain and upskill your staff
- Gain training recognition
- Sector-specific skills and training in Northern Ireland
- Developing a staff training plan - Grants Electrical Services (video)
Advantages of staff training
Find out the many benefits staff training and skills development can bring to your workers and business.
Developing and implementing effective staff training can benefit your employees and your business. By investing in your staff, even on a small training budget, you can drive down costs to your business and help increase sales and profits.
What are the benefits of staff training?
Developing your workforce and improving their skills through training can:
- increase productivity
- enable skills development and spread the skills mix across your teams and organisation
- improve the quality of work
- establish a clear standard for trained members of staff
- give staff more responsibility and ownership of their job role
- reduce faults, waste, or customer complaints with streamlined processes and more competent staff
- positively affect staff morale and motivation - see lead and motivate your staff
- reduce staff turnover and absenteeism
- help your business adapt to change and prepare for growth - see change management and planning business growth
- give you a competitive advantage over your business rivals - see increase your market share
- offer development opportunities for your employees
- help you attract top talent if your business is seen as one that values and invests in their workers - see recruiting staff
Although staff training is often mandatory for new staff members, it is just as important to offer ongoing training opportunities for long-term employees. This helps staff realise that there is an opportunity within your organisation to develop, grow, and progress. Staff training develops the skills and capabilities that individuals need for their job and improves the overall efficiency and performance of a business as a whole.
Developed withActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/advantages-staff-training
Links
How to identify staff training needs
How to identify a gap between employee knowledge and skills and training requirements using the training needs analysis technique.
To identify training that matches the specific needs of your staff and business goals, you can carry out a training needs analysis.
What is a training needs analysis?
Training needs analysis is a method used by businesses to identify training requirements in a cost-efficient way. This process involves evaluating training needs and weighing up training priority areas at all levels within a business. Training needs analysis forms the first step of the training development cycle.
Training development cycle
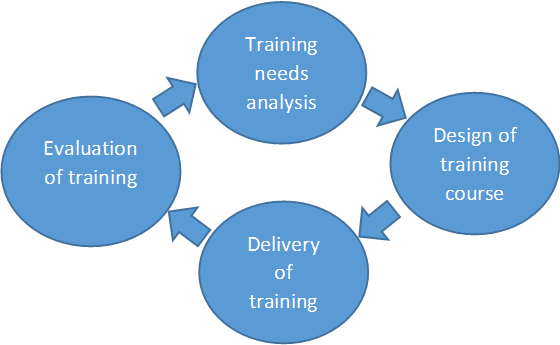
What are the stages of training needs analysis?There are three key stages of training needs analysis. These steps involve identifying the direction of the organisation, understanding the skills and knowledge of staff through a task analysis, and analysing the individual needs of each employee. These three stages of training needs analysis are explained in more detail below:
Stage 1: Organisational needs
This step evaluates the overall training needs in the business. This is where you analyse future skills needs due to changes in products, equipment, technology, and teams, or in response to economic or political factors. Upcoming changes in law or industry standards may also influence the training needs of your business.
Practical ways of identifying organisational needs are by reviewing documents and processes, setting up advisory teams, and carrying out a SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis - see a SWOT analysis example.
Stage 2: Task analysis
At this level, you compare the job requirements of your business with existing employee skills and knowledge. This will help you identify the potential skills gaps. Here, you establish how often specific tasks are performed, the level of skill and knowledge required to perform these tasks, and where and how these skills are best acquired.
Practical ways of carrying out this analysis are to create assessment centres, tests, or practical observations of employees carrying out key tasks.
Stage 3: Individual needs
At this stage, you examine the training needs of each employee. This information is most often gathered from performance reviews and appraisal systems. You may seek feedback from employees on their recommendations on how to solve problems that may be hampering their day-to-day jobs.
Other practical ways of identifying individual training requirements for your employees are through surveys, questionnaires, interviews, and focus groups. Download our SWOT analysis template with specific staff training questions (DOC, 17K)
Support to help your business with training needs analysis
Invest Northern Ireland offers help and advice to local businesses on upskilling their workforce. The training needs analysis workshops give you an insight into the tools and techniques used by learning and development professionals to analyse training needs.
Training needs analysis tutorial videos
The embedded video below is an introduction to a tutorial on training needs analysis. You can view the full Invest NI training needs analysis tutorial.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/how-identify-staff-training-needs
Links
Develop a staff training plan
How to put staff training into practice once you have identified priority areas for your employees and your business.
After you have identified the staff training required through training needs analysis, you will want to interpret the results and put your findings into practice.
Understanding the training needs analysis process
To effectively implement and deliver the benefits of your training needs analysis, you should consider the following steps:
1. Link skills requirements to your business goals and strategy
Embed the results of your training needs analysis within the direction of future training and skills development. This will ensure that you are applying your training budget effectively to the areas within your business that need it most.
2. Prioritise training needs
This is when you form the justification for your training budget by identifying how training will meet your business's key performance indicators (KPIs) - see use KPIs to assess business performance. Your initial analysis may have identified the need for staff training in multiple areas, so you will need to prioritise the parts that you will focus on first.
For example, you might consider whether the training can help employees carry out existing tasks more efficiently or to a higher standard, or if it will train staff to take on a new role with increased responsibilities. In short, you need to identify what is most important to your business.
To help identify priority training courses, you can carry out a training course priority weighting exercise. This is where you weigh up the costs and benefits of a number of training courses to identify the most beneficial one for your business. Download our training course priority weighting template (DOC, 13K).
3. Find training solutions
Establish how you will deliver the training, whether in-house or through external trainers. Some options include:
- conferences
- workshops/seminars
- e-learning/webinars
- books/journal
- coaching or mentoring
- job shadowing
- secondment
See a list of training methods to fit your business.
You can search our Events Finder for suitable training courses, workshops, webinars, and other business events.
4. Communicate
It is important to keep your employees informed of the reasons why they may have to complete certain training. Publish your training needs analysis findings and any associated training plans. Invite feedback from your employees on how they found the training they undertook.
5. Evaluate
You should evaluate the training outcomes by demonstrating how the training delivers value for money. Consider naming someone responsible for evaluating training (eg, a dedicated staff or line manager). Analyse the impact of all training on your employees, business, and productivity.
You can use a range of tools to give you qualitative and quantitative evaluation feedback. You should attempt to assess the impact of the training on employees by comparing their skills and abilities before and after training completion. The evidence you gather at this stage should be fed back to management as a demonstration of how the training provides a return on investment for the business.
Most training providers use evaluation methods that fit into the Kirkpatrick Model of Evaluation for Training (PDF, 302K), where example methods are matched to each level of evaluation.
Support to help your business with training needs analysis
Invest Northern Ireland offers help and advice to local businesses on upskilling their workforce. The training needs analysis workshops give you an insight into the tools and techniques used by learning and development professionals to analyse training needs.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/develop-staff-training-plan
Links
Training methods to fit your business
A list of training methods that may be helpful to your business and boost the skills of your staff.
An outline of some methods your business could use to help train your staff, including their advantages and disadvantages.
Training method What it involves Advantages Disadvantages Coaching By talking through a problem or task with a coach/manager, employees can arrive at a solution or better method of working - Cost-effective if done in-house
- Specific to your business's needs
- Coach or manager needs to be coached initially
- Can be time-consuming
E-learning Employees follow courses online - Employees teach themselves at their convenience
- Low cost
- Courses tend to be general rather than specific to your business's needs
Evening classes Training through classes held in the evenings - No disruption to employees during working hours
- May disrupt the work-life balance for staff
- Employees may resent having to attend classes in the evening and may not turn up
Workshops A group of employees trains together under the supervision of a trainer - typically involves explanation, examples, trying out the skill or method, reviewing what happens, and considering developments and alternatives - Employees practice solving problems
- Time-consuming - typically takes at least half a day, if not more
- May be disruptive to your business if many employees attend at the same time
- Can be expensive if you send numerous employees to workshops
Study leave Employees are given paid leave to attend courses and attain a recognised qualification
- Both the business and employee benefit
- Can be a good recruitment incentive
- Tax relief may be available on the cost, of course,
- May be difficult to decide who is eligible
Induction Formal or informal way of helping a new employee to settle down quickly in the job by introducing them to people, the business, processes, etc - Great way to help a new employee get started and understand key organisational processes
- Can be formal or informal
- Low cost
- Focused on new employees and those starting new roles
- May take up a large part of a manager's time if many new people start at the same time
Job shadowing One employee observes another employee going about their job - Low cost
- Specific to your business/their role
- There isn't a chance for hands-on practical experience to be gained
- This may give a false perspective of the job role depending on the person being shadowed and when the job shadowing is taking place.
Mentoring A more senior person typically supports an executive or manager, or director by providing advice, support, and a forum for discussing problems - Provides personal development
- Low-cost
- Limited to more senior employees
- For mentoring to be effective, the personalities and experiences of the mentor and employee need to be complementary
Networking / seminars
Employees attend a seminar on a specific topic - this can be in-house, at an industry event, or organised by a training specialist - Useful way of getting a lot of information over to a large audience
- At industry events and seminars organised by training specialists, employees can talk to their peers as competitors/partners
- Employees may be unable to discuss specific problems in front of rivals
- Retention of information may be low if there is a lot of information to convey to employees
Distance learning Employees train through courses devised by educational institutions (eg, Open University) but are not required to attend traditional classes - Increasingly web-based
- Employees can learn at their convenience
- Courses tend to be general rather than specific to your business's needs
Simulation / role-playing Typically, employees in a particular department (eg, sales) come together to take on roles to help work through possible scenarios (eg, customer complaint)
- Employees learn by doing and are prepared for possible situations at work
- Specific to your business
- Can be led by a manager
- Artificial situations remove the stress and complexities that may occur in a real-life situation
- There is always room for error when creating a situation in a training environment
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/training-methods-fit-your-business
Links
Find training courses in Northern Ireland
What to consider when choosing a suitable training provider, and where you can find training courses in Northern Ireland.
There are many organisations offering training courses throughout Northern Ireland. There are also free online training resources to help you and your staff develop their skills and make your business more competitive.
Free short-term courses (Skill Up programme)
The Department for the Economy is supporting free places on a range of fully accredited courses to help individuals retrain and improve their skills. The courses will be delivered by local universities and Further Education colleges through the Skill Up programme. See Skill Up programme: Retrain and upskill your staff.
Open University courses
The Open University has partnered with Invest Northern Ireland to provide local businesses with online training and learning resources to support upskilling in industry.
The Open University has also partnered with the Department for the Economy to offer a range of free training to help you improve your skills and wellbeing.
The Open University offers a wide range of online courses.
Other online courses
AbilityNet helps people of any age and with any disability to use technology to achieve their goals at home, at work, and in education.
Alison is a free learning platform for education and skills training. It is a not-for-profit social enterprise dedicated to making it possible for anyone, to study anything, anywhere, at any time, for free online, at any subject level.
AWS Training & Certification is free to register and offers over 500 free courses to build AWS Cloud Skills.
BBC Skillswise offers a collection of free videos and downloadable worksheets to help adult learners improve their reading, writing and numeracy skills.
BT Skills for Tomorrow offers a range of free resources anyone can use to help them stay safe, connected, and informed online.
Carnegie Trust in partnership with CILIP Library Association offers online development materials on leadership and innovation, including transformation, creativity, and innovation, influencing skills and power.
Class Central offers several thousand free online courses that have been developed by a number of top universities from across the globe, including in ICT and business.
Class of 2020 offers learning and development materials on upskilling programmes for graduates, including short courses, live webinars, business challenges, and questions and answers.
Coursera brings together courses and certificates provided online for free by a variety of universities and companies. The main focus is on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, with additional material in other areas also available.
CoursesOnline provides a huge range of training courses from the UK's leading educational providers. There are many courses to choose from, including business, IT, accountancy, human resources, marketing, and many more.
Google Digital Garage offers over 40 hours worth of training to get the digital skills you need to start your career or grow your business.
Invest NI offers a wide range of tools and business tutorials to support improvements in business processes and growth. The training needs analysis workshops also give you an insight into the tools and techniques used by learning and development professionals to analyse training needs.
Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that let learners study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom, offering mathematics, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more.
Learn My Way is a website of free online courses, built by Good Things Foundation to help people develop their digital skills.
Oxford Home Study College offers a range of fully certified provision, including cybersecurity, digital marketing, life coaching, and planning.
Training Matchmaker offers a range of free short courses, based online or across Northern Ireland, in a wide range of technical and vocational areas.
Business Events Finder
You can also search our Events Finder for business-related training, workshops, conferences, and webinars from a variety of organisations.
Choosing a training provider: what to consider
When deciding who to select for your training provider, you should consider:
- Does the trainer understand your business? Is their experience relevant to your sector?
- Is the training at the right level, is it tailored to your business, as opposed to being a generic course?
- Do the logistics of the training satisfy you? Is it hosted online or held at an appropriate venue, at the right times and dates that suit your schedule?
- Is the trainer or training business linked to any associations that can recommend them?
- Could you speak to other clients who have undergone the training?
It is likely that there will be a number of suppliers offering possible courses. You should investigate each one thoroughly to ensure they meet your requirements before going ahead.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/find-training-courses-northern-ireland
Links
Skill Up programme: Retrain and upskill your staff
Find free training opportunities to help develop the skills of your staff through the fully funded Skill Up programme.
Skill Up offers opportunities for businesses to retrain and upskill their staff by taking advantage of a range of free accredited courses. The training will be delivered by the local further and higher education providers in Northern Ireland.
Opportunities are available from entry to postgraduate levels, focusing on skills identified by industry, linked to priority economic areas, including:
- green skills
- software
- advanced manufacturing
- childcare
- health and social care
- hospitality
- transversal skills
Training courses available for 2024-25
If you are interested in the training courses available from local colleges and universities for the 2024-25 academic year, visit the provider’s website.
Queen’s University Belfast
Further information and details on how to apply for Queen's University Skill Up courses.
Ulster University
Further information and details on how to apply to the Ulster University Skill Up courses.
St Mary's University College
Further information and details on how to apply to the St Mary's University College course.
Stranmillis University College
Further information and details on how to apply to the Stranmillis University College courses.
North West Regional College
Further information and details on how to apply to the North West Regional College's Skill Up courses.
Belfast Metropolitan College
Further information and details on how to apply to the Belfast Met Skill Up courses.
Northern Regional College
Further information and details on how to apply to the Northern Regional College's Skill Up courses.
Southern Regional College
Further information and details on how to apply to the Southern Regional College's Skill Up courses.
South Eastern Regional College
Further information and details on how to apply to the South Eastern Regional College's Skill Up courses.
South West College
Further information and details on how to apply to the South West College's Skill Up courses.
The Open University
Applications for Open University Skill Up courses closed at midday on Thursday 12 September 2024.
Find further information on the Open University Skill Up courses.
Full list of Skill Up courses
For a breakdown of Skill Up courses available across the organisations, see Skill Up.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/skill-programme-retrain-and-upskill-your-staff
Links
Gain training recognition
How to get recognition and reward for your training efforts through Investors in People and various business awards.
Being recognised as an organisation that invests in its people through training and development can impress prospective customers, suppliers, and new recruits.
Investors in People
If you are seeking recognition for your training efforts and effective engagement with staff, you should consider applying for the Investors in People Awards. Investors in People is a management standard for high performance through people. The prestigious accreditation is recognised across the world as a mark of excellence.
Read more on Investors in People: the Standard for people management.
Recognition through business awards
Business awards run by various organisations and local councils usually have award categories that recognise the efforts of employers to train, develop, and look after their staff. You may find it beneficial to apply for business awards in order to have your training efforts recognised and rewarded.
Find business awards
You can find business awards by checking our business news section or business support finder.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/gain-training-recognition
Links
Sector-specific skills and training in Northern Ireland
Where to find staff training and skills development specifically tailored to your business sector.
There are several sources of sector-specific advice on skills development for employees working in a particular industry. Employers can also get involved in helping to influence how training is adapted to match the needs of their industries.
Sectoral partnerships
The purpose of sectoral partnerships is to review and develop the content of all youth traineeship and apprenticeship frameworks from level 2 to level 8 to ensure that all those involved in training are industry-ready.
There are 15 sectoral partnerships that have been established so far, including:
- Advanced Manufacturing and Engineering
- Agri-Food Manufacturing
- Built Environment
- Finance and Accounting
- Hair and Beauty
- Health and Social Care
- Hospitality and Tourism
- ICT
- Life and Health Services
- Sales and Marketing
- Business and Administration
- Childcare and Youth Work
- Civil Engineering
- Creative and Cultural
- Motor Vehicle
Employers are encouraged to become involved in sectoral partnerships to ensure apprentices and trainees are getting high-quality training that provides them with the right skills for a career in their chosen industry.
Read more on sectoral partnerships.
Sector Training Councils (STCs)
Sector Training Councils are independent employer representative bodies in Northern Ireland. Their role is to:
- articulate the skills, education, and training needs of their sectors in the short and long term
- advise on training standards required for their sectors
- work with the Department for the Economy (DfE), employers, and industry trade bodies to ensure that training needs and standards are met
You can find out more about individual Sector Training Councils at the links below:
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/sector-specific-skills-and-training-northern-ireland
Links
Staff training
Developing a staff training plan - Grants Electrical Services (video)
Grants Electrical Services, based in Mallusk, explains how they identify staff training needs and put training plans in place to develop staff skills.
Grants Electrical Services Ltd (GES), based in Mallusk, is an electrical and mechanical engineering company. They sell industrial engineering applications to customers throughout the UK and Europe. GES employs approximately 90 staff who specialise in various aspects of niche engineering.
Rachel Doherty explains the approach that GES took to identify staff training needs and develop employee skills. She describes how, following a formal analysis process, they went on to fill gaps in both staff knowledge and skills. This has helped to contribute to the company's growth. Rachel also highlights how GES has developed bespoke in-house leadership and management training that has won industry awards.
Case StudyRachel DohertyContent category
Source URL
/content/developing-staff-training-plan-grants-electrical-services-video
Links
Develop a staff training plan
In this guide:
- Staff training
- Advantages of staff training
- How to identify staff training needs
- Develop a staff training plan
- Training methods to fit your business
- Find training courses in Northern Ireland
- Skill Up programme: Retrain and upskill your staff
- Gain training recognition
- Sector-specific skills and training in Northern Ireland
- Developing a staff training plan - Grants Electrical Services (video)
Advantages of staff training
Find out the many benefits staff training and skills development can bring to your workers and business.
Developing and implementing effective staff training can benefit your employees and your business. By investing in your staff, even on a small training budget, you can drive down costs to your business and help increase sales and profits.
What are the benefits of staff training?
Developing your workforce and improving their skills through training can:
- increase productivity
- enable skills development and spread the skills mix across your teams and organisation
- improve the quality of work
- establish a clear standard for trained members of staff
- give staff more responsibility and ownership of their job role
- reduce faults, waste, or customer complaints with streamlined processes and more competent staff
- positively affect staff morale and motivation - see lead and motivate your staff
- reduce staff turnover and absenteeism
- help your business adapt to change and prepare for growth - see change management and planning business growth
- give you a competitive advantage over your business rivals - see increase your market share
- offer development opportunities for your employees
- help you attract top talent if your business is seen as one that values and invests in their workers - see recruiting staff
Although staff training is often mandatory for new staff members, it is just as important to offer ongoing training opportunities for long-term employees. This helps staff realise that there is an opportunity within your organisation to develop, grow, and progress. Staff training develops the skills and capabilities that individuals need for their job and improves the overall efficiency and performance of a business as a whole.
Developed withActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/advantages-staff-training
Links
How to identify staff training needs
How to identify a gap between employee knowledge and skills and training requirements using the training needs analysis technique.
To identify training that matches the specific needs of your staff and business goals, you can carry out a training needs analysis.
What is a training needs analysis?
Training needs analysis is a method used by businesses to identify training requirements in a cost-efficient way. This process involves evaluating training needs and weighing up training priority areas at all levels within a business. Training needs analysis forms the first step of the training development cycle.
Training development cycle

What are the stages of training needs analysis?There are three key stages of training needs analysis. These steps involve identifying the direction of the organisation, understanding the skills and knowledge of staff through a task analysis, and analysing the individual needs of each employee. These three stages of training needs analysis are explained in more detail below:
Stage 1: Organisational needs
This step evaluates the overall training needs in the business. This is where you analyse future skills needs due to changes in products, equipment, technology, and teams, or in response to economic or political factors. Upcoming changes in law or industry standards may also influence the training needs of your business.
Practical ways of identifying organisational needs are by reviewing documents and processes, setting up advisory teams, and carrying out a SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis - see a SWOT analysis example.
Stage 2: Task analysis
At this level, you compare the job requirements of your business with existing employee skills and knowledge. This will help you identify the potential skills gaps. Here, you establish how often specific tasks are performed, the level of skill and knowledge required to perform these tasks, and where and how these skills are best acquired.
Practical ways of carrying out this analysis are to create assessment centres, tests, or practical observations of employees carrying out key tasks.
Stage 3: Individual needs
At this stage, you examine the training needs of each employee. This information is most often gathered from performance reviews and appraisal systems. You may seek feedback from employees on their recommendations on how to solve problems that may be hampering their day-to-day jobs.
Other practical ways of identifying individual training requirements for your employees are through surveys, questionnaires, interviews, and focus groups. Download our SWOT analysis template with specific staff training questions (DOC, 17K)
Support to help your business with training needs analysis
Invest Northern Ireland offers help and advice to local businesses on upskilling their workforce. The training needs analysis workshops give you an insight into the tools and techniques used by learning and development professionals to analyse training needs.
Training needs analysis tutorial videos
The embedded video below is an introduction to a tutorial on training needs analysis. You can view the full Invest NI training needs analysis tutorial.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/how-identify-staff-training-needs
Links
Develop a staff training plan
How to put staff training into practice once you have identified priority areas for your employees and your business.
After you have identified the staff training required through training needs analysis, you will want to interpret the results and put your findings into practice.
Understanding the training needs analysis process
To effectively implement and deliver the benefits of your training needs analysis, you should consider the following steps:
1. Link skills requirements to your business goals and strategy
Embed the results of your training needs analysis within the direction of future training and skills development. This will ensure that you are applying your training budget effectively to the areas within your business that need it most.
2. Prioritise training needs
This is when you form the justification for your training budget by identifying how training will meet your business's key performance indicators (KPIs) - see use KPIs to assess business performance. Your initial analysis may have identified the need for staff training in multiple areas, so you will need to prioritise the parts that you will focus on first.
For example, you might consider whether the training can help employees carry out existing tasks more efficiently or to a higher standard, or if it will train staff to take on a new role with increased responsibilities. In short, you need to identify what is most important to your business.
To help identify priority training courses, you can carry out a training course priority weighting exercise. This is where you weigh up the costs and benefits of a number of training courses to identify the most beneficial one for your business. Download our training course priority weighting template (DOC, 13K).
3. Find training solutions
Establish how you will deliver the training, whether in-house or through external trainers. Some options include:
- conferences
- workshops/seminars
- e-learning/webinars
- books/journal
- coaching or mentoring
- job shadowing
- secondment
See a list of training methods to fit your business.
You can search our Events Finder for suitable training courses, workshops, webinars, and other business events.
4. Communicate
It is important to keep your employees informed of the reasons why they may have to complete certain training. Publish your training needs analysis findings and any associated training plans. Invite feedback from your employees on how they found the training they undertook.
5. Evaluate
You should evaluate the training outcomes by demonstrating how the training delivers value for money. Consider naming someone responsible for evaluating training (eg, a dedicated staff or line manager). Analyse the impact of all training on your employees, business, and productivity.
You can use a range of tools to give you qualitative and quantitative evaluation feedback. You should attempt to assess the impact of the training on employees by comparing their skills and abilities before and after training completion. The evidence you gather at this stage should be fed back to management as a demonstration of how the training provides a return on investment for the business.
Most training providers use evaluation methods that fit into the Kirkpatrick Model of Evaluation for Training (PDF, 302K), where example methods are matched to each level of evaluation.
Support to help your business with training needs analysis
Invest Northern Ireland offers help and advice to local businesses on upskilling their workforce. The training needs analysis workshops give you an insight into the tools and techniques used by learning and development professionals to analyse training needs.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/develop-staff-training-plan
Links
Training methods to fit your business
A list of training methods that may be helpful to your business and boost the skills of your staff.
An outline of some methods your business could use to help train your staff, including their advantages and disadvantages.
Training method What it involves Advantages Disadvantages Coaching By talking through a problem or task with a coach/manager, employees can arrive at a solution or better method of working - Cost-effective if done in-house
- Specific to your business's needs
- Coach or manager needs to be coached initially
- Can be time-consuming
E-learning Employees follow courses online - Employees teach themselves at their convenience
- Low cost
- Courses tend to be general rather than specific to your business's needs
Evening classes Training through classes held in the evenings - No disruption to employees during working hours
- May disrupt the work-life balance for staff
- Employees may resent having to attend classes in the evening and may not turn up
Workshops A group of employees trains together under the supervision of a trainer - typically involves explanation, examples, trying out the skill or method, reviewing what happens, and considering developments and alternatives - Employees practice solving problems
- Time-consuming - typically takes at least half a day, if not more
- May be disruptive to your business if many employees attend at the same time
- Can be expensive if you send numerous employees to workshops
Study leave Employees are given paid leave to attend courses and attain a recognised qualification
- Both the business and employee benefit
- Can be a good recruitment incentive
- Tax relief may be available on the cost, of course,
- May be difficult to decide who is eligible
Induction Formal or informal way of helping a new employee to settle down quickly in the job by introducing them to people, the business, processes, etc - Great way to help a new employee get started and understand key organisational processes
- Can be formal or informal
- Low cost
- Focused on new employees and those starting new roles
- May take up a large part of a manager's time if many new people start at the same time
Job shadowing One employee observes another employee going about their job - Low cost
- Specific to your business/their role
- There isn't a chance for hands-on practical experience to be gained
- This may give a false perspective of the job role depending on the person being shadowed and when the job shadowing is taking place.
Mentoring A more senior person typically supports an executive or manager, or director by providing advice, support, and a forum for discussing problems - Provides personal development
- Low-cost
- Limited to more senior employees
- For mentoring to be effective, the personalities and experiences of the mentor and employee need to be complementary
Networking / seminars
Employees attend a seminar on a specific topic - this can be in-house, at an industry event, or organised by a training specialist - Useful way of getting a lot of information over to a large audience
- At industry events and seminars organised by training specialists, employees can talk to their peers as competitors/partners
- Employees may be unable to discuss specific problems in front of rivals
- Retention of information may be low if there is a lot of information to convey to employees
Distance learning Employees train through courses devised by educational institutions (eg, Open University) but are not required to attend traditional classes - Increasingly web-based
- Employees can learn at their convenience
- Courses tend to be general rather than specific to your business's needs
Simulation / role-playing Typically, employees in a particular department (eg, sales) come together to take on roles to help work through possible scenarios (eg, customer complaint)
- Employees learn by doing and are prepared for possible situations at work
- Specific to your business
- Can be led by a manager
- Artificial situations remove the stress and complexities that may occur in a real-life situation
- There is always room for error when creating a situation in a training environment
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/training-methods-fit-your-business
Links
Find training courses in Northern Ireland
What to consider when choosing a suitable training provider, and where you can find training courses in Northern Ireland.
There are many organisations offering training courses throughout Northern Ireland. There are also free online training resources to help you and your staff develop their skills and make your business more competitive.
Free short-term courses (Skill Up programme)
The Department for the Economy is supporting free places on a range of fully accredited courses to help individuals retrain and improve their skills. The courses will be delivered by local universities and Further Education colleges through the Skill Up programme. See Skill Up programme: Retrain and upskill your staff.
Open University courses
The Open University has partnered with Invest Northern Ireland to provide local businesses with online training and learning resources to support upskilling in industry.
The Open University has also partnered with the Department for the Economy to offer a range of free training to help you improve your skills and wellbeing.
The Open University offers a wide range of online courses.
Other online courses
AbilityNet helps people of any age and with any disability to use technology to achieve their goals at home, at work, and in education.
Alison is a free learning platform for education and skills training. It is a not-for-profit social enterprise dedicated to making it possible for anyone, to study anything, anywhere, at any time, for free online, at any subject level.
AWS Training & Certification is free to register and offers over 500 free courses to build AWS Cloud Skills.
BBC Skillswise offers a collection of free videos and downloadable worksheets to help adult learners improve their reading, writing and numeracy skills.
BT Skills for Tomorrow offers a range of free resources anyone can use to help them stay safe, connected, and informed online.
Carnegie Trust in partnership with CILIP Library Association offers online development materials on leadership and innovation, including transformation, creativity, and innovation, influencing skills and power.
Class Central offers several thousand free online courses that have been developed by a number of top universities from across the globe, including in ICT and business.
Class of 2020 offers learning and development materials on upskilling programmes for graduates, including short courses, live webinars, business challenges, and questions and answers.
Coursera brings together courses and certificates provided online for free by a variety of universities and companies. The main focus is on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, with additional material in other areas also available.
CoursesOnline provides a huge range of training courses from the UK's leading educational providers. There are many courses to choose from, including business, IT, accountancy, human resources, marketing, and many more.
Google Digital Garage offers over 40 hours worth of training to get the digital skills you need to start your career or grow your business.
Invest NI offers a wide range of tools and business tutorials to support improvements in business processes and growth. The training needs analysis workshops also give you an insight into the tools and techniques used by learning and development professionals to analyse training needs.
Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that let learners study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom, offering mathematics, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more.
Learn My Way is a website of free online courses, built by Good Things Foundation to help people develop their digital skills.
Oxford Home Study College offers a range of fully certified provision, including cybersecurity, digital marketing, life coaching, and planning.
Training Matchmaker offers a range of free short courses, based online or across Northern Ireland, in a wide range of technical and vocational areas.
Business Events Finder
You can also search our Events Finder for business-related training, workshops, conferences, and webinars from a variety of organisations.
Choosing a training provider: what to consider
When deciding who to select for your training provider, you should consider:
- Does the trainer understand your business? Is their experience relevant to your sector?
- Is the training at the right level, is it tailored to your business, as opposed to being a generic course?
- Do the logistics of the training satisfy you? Is it hosted online or held at an appropriate venue, at the right times and dates that suit your schedule?
- Is the trainer or training business linked to any associations that can recommend them?
- Could you speak to other clients who have undergone the training?
It is likely that there will be a number of suppliers offering possible courses. You should investigate each one thoroughly to ensure they meet your requirements before going ahead.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/find-training-courses-northern-ireland
Links
Skill Up programme: Retrain and upskill your staff
Find free training opportunities to help develop the skills of your staff through the fully funded Skill Up programme.
Skill Up offers opportunities for businesses to retrain and upskill their staff by taking advantage of a range of free accredited courses. The training will be delivered by the local further and higher education providers in Northern Ireland.
Opportunities are available from entry to postgraduate levels, focusing on skills identified by industry, linked to priority economic areas, including:
- green skills
- software
- advanced manufacturing
- childcare
- health and social care
- hospitality
- transversal skills
Training courses available for 2024-25
If you are interested in the training courses available from local colleges and universities for the 2024-25 academic year, visit the provider’s website.
Queen’s University Belfast
Further information and details on how to apply for Queen's University Skill Up courses.
Ulster University
Further information and details on how to apply to the Ulster University Skill Up courses.
St Mary's University College
Further information and details on how to apply to the St Mary's University College course.
Stranmillis University College
Further information and details on how to apply to the Stranmillis University College courses.
North West Regional College
Further information and details on how to apply to the North West Regional College's Skill Up courses.
Belfast Metropolitan College
Further information and details on how to apply to the Belfast Met Skill Up courses.
Northern Regional College
Further information and details on how to apply to the Northern Regional College's Skill Up courses.
Southern Regional College
Further information and details on how to apply to the Southern Regional College's Skill Up courses.
South Eastern Regional College
Further information and details on how to apply to the South Eastern Regional College's Skill Up courses.
South West College
Further information and details on how to apply to the South West College's Skill Up courses.
The Open University
Applications for Open University Skill Up courses closed at midday on Thursday 12 September 2024.
Find further information on the Open University Skill Up courses.
Full list of Skill Up courses
For a breakdown of Skill Up courses available across the organisations, see Skill Up.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/skill-programme-retrain-and-upskill-your-staff
Links
Gain training recognition
How to get recognition and reward for your training efforts through Investors in People and various business awards.
Being recognised as an organisation that invests in its people through training and development can impress prospective customers, suppliers, and new recruits.
Investors in People
If you are seeking recognition for your training efforts and effective engagement with staff, you should consider applying for the Investors in People Awards. Investors in People is a management standard for high performance through people. The prestigious accreditation is recognised across the world as a mark of excellence.
Read more on Investors in People: the Standard for people management.
Recognition through business awards
Business awards run by various organisations and local councils usually have award categories that recognise the efforts of employers to train, develop, and look after their staff. You may find it beneficial to apply for business awards in order to have your training efforts recognised and rewarded.
Find business awards
You can find business awards by checking our business news section or business support finder.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/gain-training-recognition
Links
Sector-specific skills and training in Northern Ireland
Where to find staff training and skills development specifically tailored to your business sector.
There are several sources of sector-specific advice on skills development for employees working in a particular industry. Employers can also get involved in helping to influence how training is adapted to match the needs of their industries.
Sectoral partnerships
The purpose of sectoral partnerships is to review and develop the content of all youth traineeship and apprenticeship frameworks from level 2 to level 8 to ensure that all those involved in training are industry-ready.
There are 15 sectoral partnerships that have been established so far, including:
- Advanced Manufacturing and Engineering
- Agri-Food Manufacturing
- Built Environment
- Finance and Accounting
- Hair and Beauty
- Health and Social Care
- Hospitality and Tourism
- ICT
- Life and Health Services
- Sales and Marketing
- Business and Administration
- Childcare and Youth Work
- Civil Engineering
- Creative and Cultural
- Motor Vehicle
Employers are encouraged to become involved in sectoral partnerships to ensure apprentices and trainees are getting high-quality training that provides them with the right skills for a career in their chosen industry.
Read more on sectoral partnerships.
Sector Training Councils (STCs)
Sector Training Councils are independent employer representative bodies in Northern Ireland. Their role is to:
- articulate the skills, education, and training needs of their sectors in the short and long term
- advise on training standards required for their sectors
- work with the Department for the Economy (DfE), employers, and industry trade bodies to ensure that training needs and standards are met
You can find out more about individual Sector Training Councils at the links below:
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/sector-specific-skills-and-training-northern-ireland
Links
Staff training
Developing a staff training plan - Grants Electrical Services (video)
Grants Electrical Services, based in Mallusk, explains how they identify staff training needs and put training plans in place to develop staff skills.
Grants Electrical Services Ltd (GES), based in Mallusk, is an electrical and mechanical engineering company. They sell industrial engineering applications to customers throughout the UK and Europe. GES employs approximately 90 staff who specialise in various aspects of niche engineering.
Rachel Doherty explains the approach that GES took to identify staff training needs and develop employee skills. She describes how, following a formal analysis process, they went on to fill gaps in both staff knowledge and skills. This has helped to contribute to the company's growth. Rachel also highlights how GES has developed bespoke in-house leadership and management training that has won industry awards.
Case StudyRachel DohertyContent category
Source URL
/content/developing-staff-training-plan-grants-electrical-services-video
Links
How to identify staff training needs
In this guide:
- Staff training
- Advantages of staff training
- How to identify staff training needs
- Develop a staff training plan
- Training methods to fit your business
- Find training courses in Northern Ireland
- Skill Up programme: Retrain and upskill your staff
- Gain training recognition
- Sector-specific skills and training in Northern Ireland
- Developing a staff training plan - Grants Electrical Services (video)
Advantages of staff training
Find out the many benefits staff training and skills development can bring to your workers and business.
Developing and implementing effective staff training can benefit your employees and your business. By investing in your staff, even on a small training budget, you can drive down costs to your business and help increase sales and profits.
What are the benefits of staff training?
Developing your workforce and improving their skills through training can:
- increase productivity
- enable skills development and spread the skills mix across your teams and organisation
- improve the quality of work
- establish a clear standard for trained members of staff
- give staff more responsibility and ownership of their job role
- reduce faults, waste, or customer complaints with streamlined processes and more competent staff
- positively affect staff morale and motivation - see lead and motivate your staff
- reduce staff turnover and absenteeism
- help your business adapt to change and prepare for growth - see change management and planning business growth
- give you a competitive advantage over your business rivals - see increase your market share
- offer development opportunities for your employees
- help you attract top talent if your business is seen as one that values and invests in their workers - see recruiting staff
Although staff training is often mandatory for new staff members, it is just as important to offer ongoing training opportunities for long-term employees. This helps staff realise that there is an opportunity within your organisation to develop, grow, and progress. Staff training develops the skills and capabilities that individuals need for their job and improves the overall efficiency and performance of a business as a whole.
Developed withActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/advantages-staff-training
Links
How to identify staff training needs
How to identify a gap between employee knowledge and skills and training requirements using the training needs analysis technique.
To identify training that matches the specific needs of your staff and business goals, you can carry out a training needs analysis.
What is a training needs analysis?
Training needs analysis is a method used by businesses to identify training requirements in a cost-efficient way. This process involves evaluating training needs and weighing up training priority areas at all levels within a business. Training needs analysis forms the first step of the training development cycle.
Training development cycle

What are the stages of training needs analysis?There are three key stages of training needs analysis. These steps involve identifying the direction of the organisation, understanding the skills and knowledge of staff through a task analysis, and analysing the individual needs of each employee. These three stages of training needs analysis are explained in more detail below:
Stage 1: Organisational needs
This step evaluates the overall training needs in the business. This is where you analyse future skills needs due to changes in products, equipment, technology, and teams, or in response to economic or political factors. Upcoming changes in law or industry standards may also influence the training needs of your business.
Practical ways of identifying organisational needs are by reviewing documents and processes, setting up advisory teams, and carrying out a SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis - see a SWOT analysis example.
Stage 2: Task analysis
At this level, you compare the job requirements of your business with existing employee skills and knowledge. This will help you identify the potential skills gaps. Here, you establish how often specific tasks are performed, the level of skill and knowledge required to perform these tasks, and where and how these skills are best acquired.
Practical ways of carrying out this analysis are to create assessment centres, tests, or practical observations of employees carrying out key tasks.
Stage 3: Individual needs
At this stage, you examine the training needs of each employee. This information is most often gathered from performance reviews and appraisal systems. You may seek feedback from employees on their recommendations on how to solve problems that may be hampering their day-to-day jobs.
Other practical ways of identifying individual training requirements for your employees are through surveys, questionnaires, interviews, and focus groups. Download our SWOT analysis template with specific staff training questions (DOC, 17K)
Support to help your business with training needs analysis
Invest Northern Ireland offers help and advice to local businesses on upskilling their workforce. The training needs analysis workshops give you an insight into the tools and techniques used by learning and development professionals to analyse training needs.
Training needs analysis tutorial videos
The embedded video below is an introduction to a tutorial on training needs analysis. You can view the full Invest NI training needs analysis tutorial.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/how-identify-staff-training-needs
Links
Develop a staff training plan
How to put staff training into practice once you have identified priority areas for your employees and your business.
After you have identified the staff training required through training needs analysis, you will want to interpret the results and put your findings into practice.
Understanding the training needs analysis process
To effectively implement and deliver the benefits of your training needs analysis, you should consider the following steps:
1. Link skills requirements to your business goals and strategy
Embed the results of your training needs analysis within the direction of future training and skills development. This will ensure that you are applying your training budget effectively to the areas within your business that need it most.
2. Prioritise training needs
This is when you form the justification for your training budget by identifying how training will meet your business's key performance indicators (KPIs) - see use KPIs to assess business performance. Your initial analysis may have identified the need for staff training in multiple areas, so you will need to prioritise the parts that you will focus on first.
For example, you might consider whether the training can help employees carry out existing tasks more efficiently or to a higher standard, or if it will train staff to take on a new role with increased responsibilities. In short, you need to identify what is most important to your business.
To help identify priority training courses, you can carry out a training course priority weighting exercise. This is where you weigh up the costs and benefits of a number of training courses to identify the most beneficial one for your business. Download our training course priority weighting template (DOC, 13K).
3. Find training solutions
Establish how you will deliver the training, whether in-house or through external trainers. Some options include:
- conferences
- workshops/seminars
- e-learning/webinars
- books/journal
- coaching or mentoring
- job shadowing
- secondment
See a list of training methods to fit your business.
You can search our Events Finder for suitable training courses, workshops, webinars, and other business events.
4. Communicate
It is important to keep your employees informed of the reasons why they may have to complete certain training. Publish your training needs analysis findings and any associated training plans. Invite feedback from your employees on how they found the training they undertook.
5. Evaluate
You should evaluate the training outcomes by demonstrating how the training delivers value for money. Consider naming someone responsible for evaluating training (eg, a dedicated staff or line manager). Analyse the impact of all training on your employees, business, and productivity.
You can use a range of tools to give you qualitative and quantitative evaluation feedback. You should attempt to assess the impact of the training on employees by comparing their skills and abilities before and after training completion. The evidence you gather at this stage should be fed back to management as a demonstration of how the training provides a return on investment for the business.
Most training providers use evaluation methods that fit into the Kirkpatrick Model of Evaluation for Training (PDF, 302K), where example methods are matched to each level of evaluation.
Support to help your business with training needs analysis
Invest Northern Ireland offers help and advice to local businesses on upskilling their workforce. The training needs analysis workshops give you an insight into the tools and techniques used by learning and development professionals to analyse training needs.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/develop-staff-training-plan
Links
Training methods to fit your business
A list of training methods that may be helpful to your business and boost the skills of your staff.
An outline of some methods your business could use to help train your staff, including their advantages and disadvantages.
Training method What it involves Advantages Disadvantages Coaching By talking through a problem or task with a coach/manager, employees can arrive at a solution or better method of working - Cost-effective if done in-house
- Specific to your business's needs
- Coach or manager needs to be coached initially
- Can be time-consuming
E-learning Employees follow courses online - Employees teach themselves at their convenience
- Low cost
- Courses tend to be general rather than specific to your business's needs
Evening classes Training through classes held in the evenings - No disruption to employees during working hours
- May disrupt the work-life balance for staff
- Employees may resent having to attend classes in the evening and may not turn up
Workshops A group of employees trains together under the supervision of a trainer - typically involves explanation, examples, trying out the skill or method, reviewing what happens, and considering developments and alternatives - Employees practice solving problems
- Time-consuming - typically takes at least half a day, if not more
- May be disruptive to your business if many employees attend at the same time
- Can be expensive if you send numerous employees to workshops
Study leave Employees are given paid leave to attend courses and attain a recognised qualification
- Both the business and employee benefit
- Can be a good recruitment incentive
- Tax relief may be available on the cost, of course,
- May be difficult to decide who is eligible
Induction Formal or informal way of helping a new employee to settle down quickly in the job by introducing them to people, the business, processes, etc - Great way to help a new employee get started and understand key organisational processes
- Can be formal or informal
- Low cost
- Focused on new employees and those starting new roles
- May take up a large part of a manager's time if many new people start at the same time
Job shadowing One employee observes another employee going about their job - Low cost
- Specific to your business/their role
- There isn't a chance for hands-on practical experience to be gained
- This may give a false perspective of the job role depending on the person being shadowed and when the job shadowing is taking place.
Mentoring A more senior person typically supports an executive or manager, or director by providing advice, support, and a forum for discussing problems - Provides personal development
- Low-cost
- Limited to more senior employees
- For mentoring to be effective, the personalities and experiences of the mentor and employee need to be complementary
Networking / seminars
Employees attend a seminar on a specific topic - this can be in-house, at an industry event, or organised by a training specialist - Useful way of getting a lot of information over to a large audience
- At industry events and seminars organised by training specialists, employees can talk to their peers as competitors/partners
- Employees may be unable to discuss specific problems in front of rivals
- Retention of information may be low if there is a lot of information to convey to employees
Distance learning Employees train through courses devised by educational institutions (eg, Open University) but are not required to attend traditional classes - Increasingly web-based
- Employees can learn at their convenience
- Courses tend to be general rather than specific to your business's needs
Simulation / role-playing Typically, employees in a particular department (eg, sales) come together to take on roles to help work through possible scenarios (eg, customer complaint)
- Employees learn by doing and are prepared for possible situations at work
- Specific to your business
- Can be led by a manager
- Artificial situations remove the stress and complexities that may occur in a real-life situation
- There is always room for error when creating a situation in a training environment
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/training-methods-fit-your-business
Links
Find training courses in Northern Ireland
What to consider when choosing a suitable training provider, and where you can find training courses in Northern Ireland.
There are many organisations offering training courses throughout Northern Ireland. There are also free online training resources to help you and your staff develop their skills and make your business more competitive.
Free short-term courses (Skill Up programme)
The Department for the Economy is supporting free places on a range of fully accredited courses to help individuals retrain and improve their skills. The courses will be delivered by local universities and Further Education colleges through the Skill Up programme. See Skill Up programme: Retrain and upskill your staff.
Open University courses
The Open University has partnered with Invest Northern Ireland to provide local businesses with online training and learning resources to support upskilling in industry.
The Open University has also partnered with the Department for the Economy to offer a range of free training to help you improve your skills and wellbeing.
The Open University offers a wide range of online courses.
Other online courses
AbilityNet helps people of any age and with any disability to use technology to achieve their goals at home, at work, and in education.
Alison is a free learning platform for education and skills training. It is a not-for-profit social enterprise dedicated to making it possible for anyone, to study anything, anywhere, at any time, for free online, at any subject level.
AWS Training & Certification is free to register and offers over 500 free courses to build AWS Cloud Skills.
BBC Skillswise offers a collection of free videos and downloadable worksheets to help adult learners improve their reading, writing and numeracy skills.
BT Skills for Tomorrow offers a range of free resources anyone can use to help them stay safe, connected, and informed online.
Carnegie Trust in partnership with CILIP Library Association offers online development materials on leadership and innovation, including transformation, creativity, and innovation, influencing skills and power.
Class Central offers several thousand free online courses that have been developed by a number of top universities from across the globe, including in ICT and business.
Class of 2020 offers learning and development materials on upskilling programmes for graduates, including short courses, live webinars, business challenges, and questions and answers.
Coursera brings together courses and certificates provided online for free by a variety of universities and companies. The main focus is on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, with additional material in other areas also available.
CoursesOnline provides a huge range of training courses from the UK's leading educational providers. There are many courses to choose from, including business, IT, accountancy, human resources, marketing, and many more.
Google Digital Garage offers over 40 hours worth of training to get the digital skills you need to start your career or grow your business.
Invest NI offers a wide range of tools and business tutorials to support improvements in business processes and growth. The training needs analysis workshops also give you an insight into the tools and techniques used by learning and development professionals to analyse training needs.
Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that let learners study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom, offering mathematics, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more.
Learn My Way is a website of free online courses, built by Good Things Foundation to help people develop their digital skills.
Oxford Home Study College offers a range of fully certified provision, including cybersecurity, digital marketing, life coaching, and planning.
Training Matchmaker offers a range of free short courses, based online or across Northern Ireland, in a wide range of technical and vocational areas.
Business Events Finder
You can also search our Events Finder for business-related training, workshops, conferences, and webinars from a variety of organisations.
Choosing a training provider: what to consider
When deciding who to select for your training provider, you should consider:
- Does the trainer understand your business? Is their experience relevant to your sector?
- Is the training at the right level, is it tailored to your business, as opposed to being a generic course?
- Do the logistics of the training satisfy you? Is it hosted online or held at an appropriate venue, at the right times and dates that suit your schedule?
- Is the trainer or training business linked to any associations that can recommend them?
- Could you speak to other clients who have undergone the training?
It is likely that there will be a number of suppliers offering possible courses. You should investigate each one thoroughly to ensure they meet your requirements before going ahead.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/find-training-courses-northern-ireland
Links
Skill Up programme: Retrain and upskill your staff
Find free training opportunities to help develop the skills of your staff through the fully funded Skill Up programme.
Skill Up offers opportunities for businesses to retrain and upskill their staff by taking advantage of a range of free accredited courses. The training will be delivered by the local further and higher education providers in Northern Ireland.
Opportunities are available from entry to postgraduate levels, focusing on skills identified by industry, linked to priority economic areas, including:
- green skills
- software
- advanced manufacturing
- childcare
- health and social care
- hospitality
- transversal skills
Training courses available for 2024-25
If you are interested in the training courses available from local colleges and universities for the 2024-25 academic year, visit the provider’s website.
Queen’s University Belfast
Further information and details on how to apply for Queen's University Skill Up courses.
Ulster University
Further information and details on how to apply to the Ulster University Skill Up courses.
St Mary's University College
Further information and details on how to apply to the St Mary's University College course.
Stranmillis University College
Further information and details on how to apply to the Stranmillis University College courses.
North West Regional College
Further information and details on how to apply to the North West Regional College's Skill Up courses.
Belfast Metropolitan College
Further information and details on how to apply to the Belfast Met Skill Up courses.
Northern Regional College
Further information and details on how to apply to the Northern Regional College's Skill Up courses.
Southern Regional College
Further information and details on how to apply to the Southern Regional College's Skill Up courses.
South Eastern Regional College
Further information and details on how to apply to the South Eastern Regional College's Skill Up courses.
South West College
Further information and details on how to apply to the South West College's Skill Up courses.
The Open University
Applications for Open University Skill Up courses closed at midday on Thursday 12 September 2024.
Find further information on the Open University Skill Up courses.
Full list of Skill Up courses
For a breakdown of Skill Up courses available across the organisations, see Skill Up.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/skill-programme-retrain-and-upskill-your-staff
Links
Gain training recognition
How to get recognition and reward for your training efforts through Investors in People and various business awards.
Being recognised as an organisation that invests in its people through training and development can impress prospective customers, suppliers, and new recruits.
Investors in People
If you are seeking recognition for your training efforts and effective engagement with staff, you should consider applying for the Investors in People Awards. Investors in People is a management standard for high performance through people. The prestigious accreditation is recognised across the world as a mark of excellence.
Read more on Investors in People: the Standard for people management.
Recognition through business awards
Business awards run by various organisations and local councils usually have award categories that recognise the efforts of employers to train, develop, and look after their staff. You may find it beneficial to apply for business awards in order to have your training efforts recognised and rewarded.
Find business awards
You can find business awards by checking our business news section or business support finder.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/gain-training-recognition
Links
Sector-specific skills and training in Northern Ireland
Where to find staff training and skills development specifically tailored to your business sector.
There are several sources of sector-specific advice on skills development for employees working in a particular industry. Employers can also get involved in helping to influence how training is adapted to match the needs of their industries.
Sectoral partnerships
The purpose of sectoral partnerships is to review and develop the content of all youth traineeship and apprenticeship frameworks from level 2 to level 8 to ensure that all those involved in training are industry-ready.
There are 15 sectoral partnerships that have been established so far, including:
- Advanced Manufacturing and Engineering
- Agri-Food Manufacturing
- Built Environment
- Finance and Accounting
- Hair and Beauty
- Health and Social Care
- Hospitality and Tourism
- ICT
- Life and Health Services
- Sales and Marketing
- Business and Administration
- Childcare and Youth Work
- Civil Engineering
- Creative and Cultural
- Motor Vehicle
Employers are encouraged to become involved in sectoral partnerships to ensure apprentices and trainees are getting high-quality training that provides them with the right skills for a career in their chosen industry.
Read more on sectoral partnerships.
Sector Training Councils (STCs)
Sector Training Councils are independent employer representative bodies in Northern Ireland. Their role is to:
- articulate the skills, education, and training needs of their sectors in the short and long term
- advise on training standards required for their sectors
- work with the Department for the Economy (DfE), employers, and industry trade bodies to ensure that training needs and standards are met
You can find out more about individual Sector Training Councils at the links below:
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/sector-specific-skills-and-training-northern-ireland
Links
Staff training
Developing a staff training plan - Grants Electrical Services (video)
Grants Electrical Services, based in Mallusk, explains how they identify staff training needs and put training plans in place to develop staff skills.
Grants Electrical Services Ltd (GES), based in Mallusk, is an electrical and mechanical engineering company. They sell industrial engineering applications to customers throughout the UK and Europe. GES employs approximately 90 staff who specialise in various aspects of niche engineering.
Rachel Doherty explains the approach that GES took to identify staff training needs and develop employee skills. She describes how, following a formal analysis process, they went on to fill gaps in both staff knowledge and skills. This has helped to contribute to the company's growth. Rachel also highlights how GES has developed bespoke in-house leadership and management training that has won industry awards.
Case StudyRachel DohertyContent category
Source URL
/content/developing-staff-training-plan-grants-electrical-services-video
Links
Direct Earnings Attachment (DEA) payment schedule
In this guide:
- Staff pay
- What counts as pay?
- Issue pay slips to employees
- Statutory payments
- Guarantee pay: employee entitlement
- How to calculate guarantee pay
- Paying the National Minimum Wage and National Living Wage
- Paying workers holiday pay
- Making deductions from a worker's pay
- Direct Earnings Attachments (DEA): making deductions from an employee's salary
- Direct Earnings Attachment (DEA) payment schedule
- Calculate final pay when a worker leaves
What counts as pay?
Understand what counts as pay and what doesn't when paying a worker.
What is included as pay?
The following counts as pay:
- fees
- bonuses and commission
- holiday pay
- statutory payments, eg statutory sick, maternity, paternity, shared parental pay, adoption pay and parental bereavement pay
- overtime
- notice pay
What does not count as pay?
Pay does not include:
- loans to the worker
- refunds for expenses
- redundancy payments
- tips paid directly to the worker
- employer contributions to a pension scheme
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/what-counts-pay
Links
Issue pay slips to employees
Obligations for employers to issue itemised pay statements and penalties for not giving notice of variations in fixed deductions in staff pay.
As an employer, you are legally obliged to give each employee a written itemised pay statement, usually known as a payslip or wage slip. You must issue it at, or before, the time you pay your employee.
This right to receive an itemised pay statement does not apply to:
- people you pay who are not employees, eg freelancers and contractors
- certain other groups, including police and some people who work at sea
Pay slip: what you must include
An itemised pay statement or pay slip must show:
- gross wages or salary before deductions
- any fixed deductions - and the reasons for taking them - or the total figure for fixed deductions when you have provided a separate standing statement of the details
- any variable deductions - and the reasons for taking them
- net wages or salary payable after deductions
- a breakdown of each part-payment - such as part by cheque, part in cash
Standing statements of fixed deductions from pay
A pay statement does not have to include the amount and purpose of every separate fixed deduction every time.
However, if you don't issue a payslip that does this, you must give the employee a standing written statement of fixed deductions at least once every 12 months.
This must state for each item deducted:
- the amount
- the intervals at which the deduction is made
- the purpose or description, eg trade union subscription
You must give the employee this statement at, or before, the time of issuing the first pay statement that quotes the total figure of fixed deductions.
Variations in fixed deductions
If there is any change to an employee's fixed deductions, you must give them:
- notification in writing of the details of the change
- an amended standing statement of fixed deductions, which is then valid for up to 12 months
If a dispute occurs in the workplace between you and your employee, you may wish to seek advice and assistance from the Labour Relations Agency (LRA). The LRA may be able to help with resolving disputes before they escalate into a tribunal claim.
Tribunal claims in relation to pay statements
An employee may complain to an industrial tribunal where you have:
- Failed to give them any kind of pay statement.
- Not included all the required details in an itemised pay statement or standing statement of fixed deductions. As an employer, you can also apply to a tribunal for a decision on what should be included in a pay statement or standing statement.
- Dismissed them for seeking to enforce a right in relation to a pay statement. This right applies regardless of the employee's length of service.
Employees must make their complaint while employed by you or within three months of leaving your employment.
An industrial tribunal cannot deal with a question that is only about the accuracy of an amount in a statement.
Compensation for claims in relation to pay statements
A tribunal may award an employee compensation at its discretion if it finds that you made un-notified deductions of pay, ie deductions that did not appear on a pay statement or a standing statement.
The discretionary amount awarded will not exceed the total of the un-notified deductions during the 13 weeks immediately before the date the employee made their application to the tribunal.
All un-notified deductions enter into this calculation, whether or not they were made in breach of a contract of employment.
Arbitration services
The LRA provides an alternative to the Industrial Tribunal under the Labour Relations Agency Arbitration Scheme. Under the Scheme claimants and respondents can choose to refer a claim to an arbitrator to decide instead of going to a tribunal. The arbitrator's decision is binding as a matter of law and has the same effect as a tribunal.
Developed withActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/issue-pay-slips-employees
Links
Statutory payments
Employee entitlement to statutory payments.
An individual may be entitled to a statutory payment if they:
- become a parent, including through adoption
- are off work due to illness
- are laid-off
- to deal with issues related to domestic abuse
To qualify for statutory payments, the individual must be an employed earner, ie someone working for an employer who is liable to pay secondary Class 1 National Insurance contributions on their wages or salary.
Statutory pay for parents
To be eligible for statutory maternity, statutory paternity, statutory adoption, statutory parental bereavement, or shared parental leave and pay, the individual must:
- meet certain qualifying criteria relating to minimum earnings, continuous employment, and - in paternity and adoption cases - their relationship with the child and the biological mother/other adoptive parent
- comply with certain notification rules
Statutory sick pay
Under certain conditions, you may have to pay statutory sick pay to an employee.
This is the minimum level of payment you must make to someone who is off work through illness. Their contract with you may also entitle them to more than this.
New pending legislation - Statutory Safe Leave
The passing into law of the Domestic Abuse (Safe Leave) Act (Northern Ireland 2022 will mean that employers in Northern Ireland will have the duty to offer at least 10 days of paid leave for victims of domestic abuse each leave year for the purposes of dealing with issues related to domestic abuse.
Although the commencement date of the legislation is yet to be confirmed, employers can take steps within their businesses to prepare for it by creating an environment where employees feel safe to disclose that they are experiencing domestic abuse. See workplace policy on domestic and sexual abuse.
Statutory payments: further information
Find out more about qualifying for:
- Maternity leave and pay
- Adoption leave and pay
- Paternity leave and pay
- Statutory sick pay and leave
- Shared parental leave and pay
- Parental Bereavement Leave and Pay
You can also call the HMRC Employer Helpline on Tel 0300 200 3200.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/statutory-payments
Links
Guarantee pay: employee entitlement
What guarantee pay is and who is eligible for it.
You may have to pay your employees a guarantee payment if you cannot provide them with employment on a day when they would normally work for you under their contract of employment.
This is to compensate for the loss, through no fault of their own, of what they would have earned in normal circumstances.
Entitlement to guarantee pay
Individuals are entitled to guarantee pay if they meet the following conditions:
- they are an employee, ie they are working under a contract of employment - see employment status
- they are not an excluded employee, as defined below
- they have worked for at least one month's continuing employment up to the day before the one that guarantee payment is being claimed for
- they have normal working hours and are normally required to work in accordance with their contract of employment
- the day they claim for is not a day they were on holiday, were sick, or not required to work under the contract of employment
- they must not have worked at all on what would be a normal working day (a day being the 24-hour period from midnight to midnight)
- the absence of work was not caused by industrial action, involving any of your other employees or employees working for your subsidiary or parent company
- the reason they did not work is because there was a recession in the employer's business or anything else disrupted the normal working of the employer's business, for example, a natural disaster or failing power supply
- they have not unreasonably refused an offer from you of suitable alternative work - this can be work other than what they normally do
- they have complied with any reasonable requirements imposed by you to ensure their services are available
Excluded employees
You do not have to pay guarantee pay to excluded employees. These are:
- masters and crew members involved in share fishing who are paid solely by a share in the profits or gross earnings of a fishing vessel
- members of the police service and armed forces
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/guarantee-pay-employee-entitlement
Links
How to calculate guarantee pay
How to work out the amount of guarantee pay you must pay your staff and what the exceptions are.
To calculate guarantee pay, multiply the number of hours your employee would normally have worked on the day in question (as stated in their terms and conditions of employment) by their hourly rate.
Statutory guarantee pay is subject to an upper limit of £39 per day. This amount changes every year. Statutory entitlement is limited to five days in any three-month period. This entitlement is reduced pro rata for employees who work fewer than five days a week.
You do not have to pay guarantee pay for voluntary overtime.
Exemptions from the statutory guarantee pay provisions
The Department for the Economy can grant an exemption from the statutory provisions if you have your own collective agreement. For this agreement to be valid, all parties to the agreement must be making the application for exemption, ie you and your employee, and the guarantee payment must be as favourable overall to your employees as the statutory provisions.
The agreement must also provide a complaints procedure that either includes a right to independent arbitration in the event of a deadlock or specifies that your employee may complain to an industrial tribunal - in which case the tribunal would have jurisdiction over the agreement.
The Employment Rights (NI Order) 1996 also provides for an exemption being granted by the Department of Agriculture, Environment & Rural Affairs (DAERA) where there is an Agricultural wages order under which employees to whom the order relates have a right to guaranteed remuneration.
You do not have to pay statutory guarantee pay on top of any contractual entitlement.
Employment protection rights
It is unlawful to dismiss an employee for seeking guarantee pay.
It is also unlawful not to pay guarantee pay to an employee if they are entitled to it.
In both of these cases, the employee can complain to an industrial tribunal.
Arbitration services
The Labour Relations Agency (LRA) provides an alternative to the Industrial Tribunal under the Labour Relations Agency Arbitration Scheme. Under the Arbitration Scheme claimants and respondents can choose to refer a claim to an arbitrator to decide instead of going to a tribunal. The arbitrator's decision is binding as a matter of law and has the same effect as a tribunal.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/how-calculate-guarantee-pay
Links
Paying the National Minimum Wage and National Living Wage
You must ensure you pay your workers at least the National Minimum Wage or National Living Wage depending on their eligibility.
Most workers who are above compulsory school age must be paid at least the National Minimum Wage or National Living Wage.
The rate you must pay varies depending on the worker's circumstances.
To find out how to calculate a worker's pay for the purpose of comparing it to the appropriate minimum wage rate, see National Minimum Wage and National Living Wage - calculating minimum wage pay.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/paying-national-minimum-wage-and-national-living-wage
Links
Paying workers holiday pay
Employees' entitlement to paid annual leave.
A worker is entitled to take at least 5.6 weeks paid annual leave.
This is equivalent to, for example:
- 28 days for those who work five days a week
- 16.8 days for those who work 3 days a week
Bank and public holidays
The minimum paid annual leave entitlement can include bank and public holidays.
Workers have no statutory right to take a day's leave on any bank or public holiday or to higher rates of pay if they work on such days.
You must set out in an employee's written statement of employment their holiday entitlement, including arrangements for bank and public holidays, and holiday pay.
Carrying over annual leave
Workers must take at least four weeks' annual leave. Any additional leave may be carried over to the following leave year where this is agreed by you and your worker.
Payment in lieu of annual leave
The only time you can make a payment in lieu of any outstanding holiday is when a worker's employment ends.
Rates of holiday pay
The rate of holiday pay is generally the normal rate for the worker. So for those workers who are paid monthly, their annual salary is divided into 12 equal payments and when they take a holiday it has no effect on their pay slip.
Case law has determined that guaranteed and non-guaranteed overtime should be considered when calculating a worker's statutory holiday pay. Further, the Court of Appeal in Northern Ireland determined that where voluntary overtime constitutes part of an employee's 'normal working week' - this also may need to be taken into account when calculating holiday pay.
You only have to work out a special payment where your workers have varying pay rates, such as piece work. In those cases, the holiday pay will be equal to the average rate over the 12 weeks before the holiday.
Any week in which no pay was due should be replaced by the last previous week in which pay was received to bring the total to twelve.
This only applies to the statutory holiday periods. If you offer extra leave over and above the 5.6 weeks (including bank and public holidays) the rate of pay for these can be whatever is agreed with your employees.
Rolled-up holiday pay
It is unlawful not to pay a worker while they are on holiday and instead include an amount for holiday pay in the hourly rate of pay - something known as 'rolled-up holiday pay'.
You must always pay a worker their normal pay while they are actually taking their leave.
No fixed hours
If your workers do casual work with no normal hours, for example, on a zero-hours contract, the holiday pay of each worker will be based on the average pay they got over the previous 12 weeks.
These should be weeks in which they were paid. If they were not paid in one of those 12 weeks, because they did not work, the last paid week before that should be used to calculate their holiday pay.
Term-time or part-year workers
Recent case law has determined workers employed on a continuous contract throughout the year, and who work for varying hours during certain weeks of the year, such as those who work only term-time, are entitled to 5.6 weeks of leave each year. This entitlement applies regardless of the fact that there are some weeks in the year when they do not work.
In such instances holiday pay is calculated by averaging the pay received during the 12 weeks prior to the commencement of their leave. If there are weeks during the 12-week period where no pay was received, these weeks are disregarded and the employer must count back to include a total of 12 weeks in which pay was received.
Although there may be times when a part-year worker receives a higher payment than a full-time worker - this is compliant with the Part-Time Workers (Prevention of Less favourable Treatment) Regulations (Northern Ireland) 2000, as the part-time worker is not being treated less favourably. There is no legislative provision to prevent part-time workers from being treated more favourably.
Developed withActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/paying-workers-holiday-pay
Links
Making deductions from a worker's pay
Legally required deductions such as National Insurance and income tax.
You must not make deductions from a worker's pay unless:
- they are legally authorised, eg PAYE (Pay As You Earn) income tax, National Insurance contributions, deductions from earnings orders, student loan repayments
- they are allowed by the worker's contract - workers must have a copy of the relevant contractual term or a written explanation before you make the deduction
- they have agreed to the deduction in writing before the deduction was made
You don't always have to meet these conditions, for example, when:
- you make deductions to refund an overpayment of wages or expenses
- the worker is on strike
- the deduction is to satisfy a court order, eg to recover debts
Deductions for child maintenance
The Child Maintenance Service (CMS) of the Department for Communities (DfC) may ask you to make deductions from an employee's pay for child maintenance purposes. They may issue you with a deduction from the earnings order and ask you to establish a regular pattern of payments. See how to make child maintenance deductions from an employee's pay.
Direct Earnings Attachments
You may be asked as an employer to deduct benefit overpayments, including social fund loans, that an employee owes the Department for Communities (DfC) from their pay. Read more on Direct Earnings Attachments: making deductions from an employee's pay.
Deductions from the wages of retail workers
If your workers do retail work, you may make deductions from wages to recover cash shortages or stock deficiencies only if, in addition to meeting the above conditions, you:
- inform the worker, in writing, of the total shortfall you are recovering before you make the deduction
- issue a written demand on a payday for the repayment
- make the deduction - or the first in a series - no sooner than their first payday after telling them of the shortfall or, if you tell them on a payday, not before that day
- do not deduct more than one-tenth of the worker's gross pay on any given payday - you can recover any remaining shortfall on future paydays (note that one-tenth of gross pay does not apply when making the final payment on termination of employment)
- make the first deduction within 12 months of discovering the shortage
You should ensure that any deductions for shortages or stock deficiencies are not made unless you have conducted a thorough investigation to establish that the employee is liable for these. You should also take care when making any deductions not to breach minimum wage, as deductions must not reduce your employee's pay below the current minimum wage rate.
Developed withActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/making-deductions-workers-pay
Links
Direct Earnings Attachments (DEA): making deductions from an employee's salary
The Department for Communities will write to you if you need to make DEA deductions for an employee.
Difficulty repaying a benefit or Welfare Supplementary Payment overpayment, Social Fund, or Discretionary Support Loan?
If your employee is having difficulty repaying their benefit overpayment, Social Fund, or Discretionary Support loan, they should act as soon as possible. Even if they have contacted the Department for Communities (DfC) before, they can get in touch to ask them to consider reducing the amount they repay.
If an employee is struggling financially or knows their repayments are no longer affordable, they can ask for them to be reduced by contacting Debt Management.
Further information is also available on financial support and advice from DfC.
As an employer, you may be asked to make deductions from an employee's pay towards benefit overpayments and Social Fund loans that the employee owes to the Department for Communities (DfC). This method of recovery is known as a Direct Earnings Attachment or DEA.
The DfC Debt Management will write to you with an instruction to set up and maintain a DEA if any of your employees are affected.
How a DEA works
Any instruction you receive from the DfC will state the total amount to be recovered from the employee's salary. It is important to note that this is the total amount owed to the DfC and not a deduction amount which must be calculated as a percentage of net earnings. To operate the DEA, you will need to take the following steps:
- for each salary cycle, calculate how much to deduct from your employee's salary
- check if your employee has other debt orders to pay and if they take priority over a DEA
- advise your employee that money will be deducted from their salary in respect of monies owed to the DfC
- deduct the money from your employee's salary
- pay the money to DfC no later than the 19th day of the month following deduction in your payroll
- continue to make employee deductions and payments to the DfC until the total amount stated in the instruction has been repaid or the DfC tells you to stop
Record keeping for DEA
You must keep a record of deductions and tell the DfC when an employee leaves your company.
You could be fined up to £1,000 if you don't make DEA deductions when requested to.
Download Direct Earnings Attachment employer guidance (PDF, 1.0MB).
Employer help with DEA or payments
You can also call the employer helpline if you have questions about how to run a DEA or pay the DfC:
Employer Helpline
0800 587 1322 (Monday to Friday, 9am to 4pm)
Calculating the DEA deduction
There are two deduction percentage rates which may be used for calculation - Standard Rate and Higher Rate.
The instruction from DfC Debt Management will let you know which of these rates to apply. The rate may change throughout the life of the DEA, from Standard to Higher and vice versa, and you will be notified of this by letter.
To calculate the deductions from your employee's salary, for each salary cycle you'll have to:
- work out the employee's earnings after tax, class 1 National Insurance, and workplace pension contributions (net earnings)
- check if the employee has other debt orders and if they take priority over a DEA
- use the tables below (standard or higher) to establish the appropriate percentage deduction rate
- multiply the net earnings figure by the percentage rate to calculate the DEA amount
Note: if you are calculating a DEA based on a daily rate, you must also multiply the daily rate figure by the number of days in the pay period.
If payments are made every two or four weeks, calculate weekly pay and deduct the percentage in the table.
If the total of all deductions is more than 40% of the employee's net earnings, the DEA must be adjusted.
Deductions from earnings rate
AMOUNT OF NET EARNINGS
(Net earnings are gross pay, less income tax, Class 1 National Insurance, and superannuation contributions)
Deduction from Earnings Rate
(Standard)
Rate to apply (% of net earnings)
Deduction from Earnings Rate
(Higher)
Rate to apply (% of net earnings)
Daily Earnings
Weekly Earnings
Monthly Earnings
Up to £15
Up to £100
Up to £430
Nil
5% Between £15.01 and £23
Between £100.01 and £160
Between £430.01 and £690
3%
6% Between £23.01 and £32
Between £160.01 and £220
Between £690.01 and £950
5%
10% Between £32.01 and £39
Between £220.01 and £270
Between £950.01 and £1,160
7%
14% Between £39.01 and £54
Between £270.01 and £375
Between £1,160.01 and £1,615
11%
22% Between £54.01 and £75
Between £375.01 and £520
Between £1,615.01 and £2,240
15%
30% £75.01 or more
£520.01 or more
£2,240.01 or more
20%
40%
What counts as earnings?
When calculating DEA payments, you should include as earnings:
- wages and salary
- fees
- bonuses
- commission
- overtime pay
- occupational pensions if paid with wages or salary
- compensation payments
- Statutory Sick Pay
- most other payments on top of wages
- pay in lieu of notice
Don't count:
- Statutory Maternity Pay
- Statutory Adoption Pay
- Ordinary or Additional Paternity Pay
- guaranteed minimum pension
- any money that the employee gets from the Government e.g. benefits, pensions or credits
- Statutory Redundancy Pay
- expenses
Developed withActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/direct-earnings-attachments-dea-making-deductions-employees-salary
Links
Direct Earnings Attachment (DEA) payment schedule
The supporting payment schedule for a DEA that must be completed and issued in order to ensure that the correct payment is allocated to the correct debtor account.
The Department for Communities (DfC) requires that a supporting payment schedule for Direct Earnings Attachment (DEA) be completed and issued in order to ensure that the correct payment is allocated to the correct debtor account. This schedule is only required if you are making one overall payment in respect of several employees. However, if you are making a single DEA payment by cheque, you must send a payment schedule.
For a single DEA payment, please ensure that you include your employee's National Insurance number and not their name.
DfC Debt Management has introduced an email route to receive payment schedules from employers, this is the preferred way for payment schedules to be sent.
DEA payment schedule template
Download the payment schedule template for DEA (XLSX, 82K).
For data security reasons the data required for the email payment schedule is slightly different to that on the paper schedule. By restricting the data recorded on the email payment schedule DfC Debt Management will still have enough information to correctly allocate payments to our customer records, whilst minimising the risk of personal data being fraudulently used should the email fall into the hands of a third party. Schedules do not need to be encrypted before emailing.
The postal route for sending payment schedules remains in place and a schedule template for use when forwarding schedules is available in appendix 2 of the DEA: a guide for employers (PDF, 1.0MB).
Developed withActionsContent category
Source URL
/content/direct-earnings-attachment-dea-payment-schedule
Links
Calculate final pay when a worker leaves
Deductions to make from outstanding pay owed when an employee leaves the business.
When a worker leaves your employment, you must give them:
- any outstanding pay, including overtime
- pay in lieu for any untaken holiday
- bonus payments, if earned
- any statutory sick pay, if they are entitled to it
- pay instead of notice if you do not require them to work their notice period - note that the contract of employment must provide for this, otherwise the employee must agree to it
- redundancy payment, if due
If the worker leaves before or during their statutory maternity or adoption pay period, you must also start paying - or continue to pay - them statutory maternity or adoption pay.
You could also give them:
- a pension refund, depending on the rules of the scheme
- a lump-sum payment as compensation for loss of their job
- an enhanced redundancy payment if you have made them redundant - this might be either contractual or paid on a discretionary, and non-discriminatory, case-by-case basis
What you should deduct from a worker's final pay
You must deduct the following items from what you owe the worker:
- income tax
- relevant National Insurance contributions
You might also need to consider deductions in respect of matters such as:
- money given for season ticket loans
- any other outstanding loans
- amounts to be paid under any car leasing agreements
Developed withActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/calculate-final-pay-when-worker-leaves
Links
Local support for employers and migrant workers
In this guide:
- Employing migrant workers in Northern Ireland
- Advantages of employing migrant workers
- Recruiting migrant workers
- Taking migrant workers through their induction
- How to support migrant workers in your business
- Local support for employers and migrant workers
- Recruiting and supporting migrant workers - Avondale Foods (video)
Advantages of employing migrant workers
There are many advantages to employing migrant workers including gaining access to new skills and knowledge.
A new immigration system applies to people arriving in the UK from 1 January 2021. EU citizens moving to the UK to work will need to get a visa in advance. Employers need a sponsor licence to hire most workers from outside the UK.
Please note: this requirement excludes Irish citizens and those who already have settled or pre-settled status under the EU Settlement Scheme.
See right to work checks: employing EU, EEA and Swiss citizens.
Business benefits of employing migrant workers
Migrant workers can make a positive contribution to business performance and productivity. They can also bring culturally unique and complementary skills and knowledge to your business.
Some of the advantages of employing migrant workers in your business include:
Filling skills gaps
Fulfiling existing contracts and taking on more work through new skills and talent.
Increased diversity
This can bring many advantages such as different perspectives, better problem-solving skills, increased creativity, and innovation. A diverse workforce can also help you attract talent, customers, and clients.
Knowledge sharing
Increasing access to international knowledge and supporting the upskilling of co-workers.
Expansion into new markets
Strengthening contacts in international markets and local networks through new language skills and cultural awareness.
Access a larger pool of workers
By expanding into other geographical areas you are no longer limiting the talent pool to your country. You increase your chances of finding the right employees for the job in a larger talent pool.
Better problem-solving
Hiring workers from different countries and cultures can help increase your company's problem-solving capabilities. Migrant workers can offer new perspectives on old problems helping you find new and innovative solutions.
Enrichment from different cultures
Creating a more diverse workforce with varied experiences and ways of working.
Greater flexibility
People from different cultures are often more flexible regarding working hours.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/advantages-employing-migrant-workers
Links
Recruiting migrant workers
The steps you should take as an employer when recruiting migrant workers.
A new immigration system applies to people arriving in the UK from 1 January 2021. EU citizens moving to the UK to work will need to get a visa in advance. Employers need a sponsor licence to hire most workers from outside the UK.
Please note: this requirement excludes Irish citizens and those who already have settled or pre-settled status under the EU Settlement Scheme.
See right to work check: employing EU, EEA, and Swiss citizens.
Under the Race Relations (NI) Order 1997, it is unlawful for an employer to discriminate on the grounds of race against a job applicant:
- in the arrangements made for deciding who should be offered employment;
- in the terms in which employment is offered; or
- by refusing to offer employment
Preventing illegal migrant working
All employers have a responsibility to prevent illegal migrant working. You must check the entitlement of everyone you plan to employ to work in the UK.
See checking a job applicant's right to work.
Job descriptions
When putting together a job description - ensure that it is a fair reflection of the role and that all criteria are essential to the job.
You should also communicate the overseas qualifications that would be considered for the role and determine any level of English required.
Job advertising
When advertising for a role, you should ensure it is advertised as widely as possible.
Jobs and Benefits Offices throughout Northern Ireland offer a range of free services to help employers find suitable staff and will assist with placing job advertisements both locally and in other countries.
Find your local Jobs and Benefits Office.
You should also ensure advertisements are written in plain English and that the wording, criteria, and images cannot be considered discriminatory.
In addition, you could also run recruitment information sessions to assist potential employees with completing applications and providing monitoring information.
You could also make sure your website is user-friendly for migrant workers by translating the job vacancy section.
You could consider alternative recruitment methods such as roadshows, open days, or even virtual job fairs to actively recruit in other countries.
Recruitment and selection
When carrying out interviews or selection testing:
- consider language issues eg abbreviations that are only understood locally
- make sure your recruitment process schedule allows time to make appropriate travel arrangements
When assessing qualifications and references, you should develop a procedure for qualification equivalency checking. See get your EU professional qualification recognised in the UK.
You could use an organisation such as the European Qualifications Framework or UK ENIC, the designated UK national agency for the recognition and comparison of international qualifications and skills, to assist with evaluating the comparative value of qualifications gained overseas.
ActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/recruiting-migrant-workers
Links
Taking migrant workers through their induction
When taking a migrant worker through their induction, you should remember that they may require additional support.
A new immigration system applies to people arriving in the UK from 1 January 2021. EU citizens moving to the UK to work will need to get a visa in advance. Employers need a sponsor licence to hire most workers from outside the UK.
Please note: this requirement excludes Irish citizens and those who already have settled or pre-settled status under the EU Settlement Scheme.
See right to work checks: employing EU, EEA and Swiss citizens.
When carrying out an induction with a migrant worker, you should remember that they may need additional support.
Beginning employment in a new organisation can be difficult for anyone but working in a new country can bring additional challenges.
Effectively assisting new employees should mean that they adapt more easily to their new roles and become more productive.
Planning an induction
When planning an induction, take into account if the individual's first language is not English.
You should also be sensitive to cultural or religious customs and make sure the process is not discriminatory in any way.
Putting together a welcome pack is a good way to provide key information about your business, employment documents, and facilities. See new starter pack for staff.
It may be useful to include information about living in Northern Ireland and English language classes in the pack. See tailoring the induction to the worker.
Further help following the induction
Following up with new employees after an induction can give you the opportunity to help further with their integration or any queries they may have eg accommodation, childcare, or banking issues.
It may also be useful to link them up with another employee who could act as a 'mentor' and provide further information and support about the business and the local area.
ActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/taking-migrant-workers-through-their-induction
Links
How to support migrant workers in your business
There are many ways you can support migrant workers in your business including having the correct policies and providing appropriate training.
A new immigration system applies to people arriving in the UK from 1 January 2021. EU citizens moving to the UK to work will need to get a visa in advance. Employers need a sponsor licence to hire most workers from outside the UK.
Please note: this requirement excludes Irish citizens and those who already have settled or pre-settled status under the EU Settlement Scheme.
See right to work checks: employing EU, EEA, and Swiss citizens.
Migrant workers may face a number of unique challenges in the workplace, including communication or language barriers, cultural differences or their international qualifications not being recognised in Northern Ireland. As an employer, you should be aware of these challenges and identify ways in which you can support any migrant workers you may employ.
Implement policies and procedures
Your policies and procedures should promote equality of opportunity in the workplace, especially your equal opportunities and harassment policies and procedures.
See disciplinary, grievance, bullying and harassment policies.
You should have equality and diversity policies in place and ensure they are followed and understood across the business. See equality and diversity workplace policies.
Encouraging input from staff when creating and reviewing policies can be useful in ensuring that they are implemented throughout the organisation.
Model policy templates
The Equality Commission provides free model policies that are available to download from the Equality Commission's website.
You should also regularly review these policies in relation to relevant issues such as language and religious and cultural needs.
Racial equality plan template
A good way to take practical action to help you implement your policies and procedures in order to benefit migrant workers and members of other racial or ethnic groups is to develop a racial equality action plan. Find further guidance from the Equality Commission on equality plans, including a racial equality plan template that you can download and adapt for your organisation.
Provide equality and diversity training
Providing equality and diversity training for all workers could also help to embed the correct procedures and values into your business. You should also include bullying, harassment, and dignity at work within this training.
Bullying and harassment training specifically for line managers/supervisors would help them spot signs of bullying or harassment and decide on the best way to deal with any issues that may arise.
Line managers should also monitor the effectiveness of staff training and be proactive in addressing any issues that arise eg a worker having difficulty mixing with other staff.
In addition, having a suitable induction process set up for non-UK nationals is essential in helping them to integrate and settle into the business and the new culture.
See taking migrant workers through their induction.
Focus on language and communication
You should ensure migrant workers understand their legal rights and responsibilities, even if this means translating important documents.
You could also use a mentoring system, where less experienced workers are paired with experienced colleagues who speak the same language.
You could also put flexible arrangements in place to allow attendance at courses in 'workplace English' for speakers of other languages. This would help to reduce the need for translation.
English for Speakers of Other Languages (ESOL) classes focus on speaking and listening, reading and writing, vocabulary and punctuation, and grammar. There are courses available at different levels of competence.
You could also help with integration among staff by organising team events where everyone can get involved eg fundraising events.
Provide training and development opportunities
It is good practice to ensure all employees have the opportunity to develop and enhance their skills, both personally and professionally.
See staff training.
ActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/how-support-migrant-workers-your-business
Links
Local support for employers and migrant workers
Support organisations that are available to Northern Ireland employers and migrant workers.
A new immigration system applies to people arriving in the UK from 1 January 2021. EU citizens moving to the UK to work will need to get a visa in advance. Employers need a sponsor licence to hire most workers from outside the UK.
Please note: this requirement excludes Irish citizens and those who already have settled or pre-settled status under the EU Settlement Scheme.
See right to work checks: employing EU, EEA, and Swiss citizens.
There is a variety of support available to both employers and migrant workers in Northern Ireland.
The Careers Service
The Careers Service, within the Department for the Economy (DfE), provides an impartial, all-age service to help with making informed choices about future career paths.
Find out more about the Careers Service.
Qualifications Equivalence Service
The Department for Communities (DfC) provides the Qualifications Equivalence Service if you are a resident in Northern Ireland and need to check your qualifications against UK equivalents. This free service is accessible through your local Jobs and Benefits office or JobCentre.
A member of staff will arrange a check against UK National Recognition Information Centre (NARIC) database on your behalf, and provide you with comparison information and advice on your specific qualifications.
Not resident in Northern Ireland
If you are a non-UK national from a member state within the EU, EEA or Switzerland with professional qualifications and wish to work in Northern Ireland you may be eligible, under the EU Directive on the Mutual Recognition of Professional Qualifications (Directive 2005/36/EC), for automatic or general recognition of your qualifications depending on your profession.
For further details, see are your country's qualifications recognised in the UK?
The UK European Network of Information Centre (UK ENIC)
UK ENIC (formerly UK NARIC) is responsible for providing information and advice on vocational, academic and professional skills qualifications worldwide.
Managed on behalf of the UK Government, it is provided to help people who are looking for a job or wish to undertake further study.
The Department for Business and Trade
Some professions in the UK are regulated. This can mean there is a legal requirement to have certain qualifications or experience. Other professions are regulated by chartered bodies granting a certain status.
The Department for Business and Trade has a tool to help you check which professions are regulated in the UK and find contact details for regulators of those professions.
Equality Commission
The Equality Commission provides practical advice to employer and service providers on how they can manage the equality implications of employing and managing staff.
This includes helping you to develop a practical and flexible framework to assess your current policies in relation to race and migrant workers and using equality indicators to identify gaps in your policies.
In addition, through the employer training programme, employers can also attend training seminars and information sessions on a wide range of equality issues including managing bullying and harassment and recruiting fairly.
Labour Relations Agency
The Labour Relations Agency (LRA) provides an impartial and confidential employment relations service, including advice on good employment practices and assistance with the development and implementation of policies and procedures.
The LRA also helps to resolve workplace disputes through its conciliation, mediation and arbitration services.
In addition, the LRA hosts a free events programme of best practice seminars, workshops and briefings on a broad range of employment issues throughout the year.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/local-support-employers-and-migrant-workers
Links
Employing migrant workers in Northern Ireland
Recruiting and supporting migrant workers - Avondale Foods (video)
Mia McKeown from Lurgan-based business Avondale Foods explains how they recruit, employ, and support migrant workers in their business.
Avondale Foods, based in Lurgan Co. Armagh, is one of the UK's leading manufacturers and suppliers of coleslaw, wet salads, side salads, vegetable accompaniments, soups, sauces, and mayonnaise to retail and food-service customers throughout Britain and Ireland under their Country Kitchen brand name. Their clients include Waitrose, Marks and Spencer, Sainsbury, Tesco and Asda.
Avondale Foods employs a large number of migrant workers who make up around 60% of their workforce. Here, Mia McKeown, the Human Resources Manager, explains how Avondale Foods recruits fairly, highlights how they support their migrant workers, and outlines the legal considerations for employers.
Case StudyMia McKeownContent category
Source URL
/content/recruiting-and-supporting-migrant-workers-avondale-foods-video
Links
How to support migrant workers in your business
In this guide:
- Employing migrant workers in Northern Ireland
- Advantages of employing migrant workers
- Recruiting migrant workers
- Taking migrant workers through their induction
- How to support migrant workers in your business
- Local support for employers and migrant workers
- Recruiting and supporting migrant workers - Avondale Foods (video)
Advantages of employing migrant workers
There are many advantages to employing migrant workers including gaining access to new skills and knowledge.
A new immigration system applies to people arriving in the UK from 1 January 2021. EU citizens moving to the UK to work will need to get a visa in advance. Employers need a sponsor licence to hire most workers from outside the UK.
Please note: this requirement excludes Irish citizens and those who already have settled or pre-settled status under the EU Settlement Scheme.
See right to work checks: employing EU, EEA and Swiss citizens.
Business benefits of employing migrant workers
Migrant workers can make a positive contribution to business performance and productivity. They can also bring culturally unique and complementary skills and knowledge to your business.
Some of the advantages of employing migrant workers in your business include:
Filling skills gaps
Fulfiling existing contracts and taking on more work through new skills and talent.
Increased diversity
This can bring many advantages such as different perspectives, better problem-solving skills, increased creativity, and innovation. A diverse workforce can also help you attract talent, customers, and clients.
Knowledge sharing
Increasing access to international knowledge and supporting the upskilling of co-workers.
Expansion into new markets
Strengthening contacts in international markets and local networks through new language skills and cultural awareness.
Access a larger pool of workers
By expanding into other geographical areas you are no longer limiting the talent pool to your country. You increase your chances of finding the right employees for the job in a larger talent pool.
Better problem-solving
Hiring workers from different countries and cultures can help increase your company's problem-solving capabilities. Migrant workers can offer new perspectives on old problems helping you find new and innovative solutions.
Enrichment from different cultures
Creating a more diverse workforce with varied experiences and ways of working.
Greater flexibility
People from different cultures are often more flexible regarding working hours.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/advantages-employing-migrant-workers
Links
Recruiting migrant workers
The steps you should take as an employer when recruiting migrant workers.
A new immigration system applies to people arriving in the UK from 1 January 2021. EU citizens moving to the UK to work will need to get a visa in advance. Employers need a sponsor licence to hire most workers from outside the UK.
Please note: this requirement excludes Irish citizens and those who already have settled or pre-settled status under the EU Settlement Scheme.
See right to work check: employing EU, EEA, and Swiss citizens.
Under the Race Relations (NI) Order 1997, it is unlawful for an employer to discriminate on the grounds of race against a job applicant:
- in the arrangements made for deciding who should be offered employment;
- in the terms in which employment is offered; or
- by refusing to offer employment
Preventing illegal migrant working
All employers have a responsibility to prevent illegal migrant working. You must check the entitlement of everyone you plan to employ to work in the UK.
See checking a job applicant's right to work.
Job descriptions
When putting together a job description - ensure that it is a fair reflection of the role and that all criteria are essential to the job.
You should also communicate the overseas qualifications that would be considered for the role and determine any level of English required.
Job advertising
When advertising for a role, you should ensure it is advertised as widely as possible.
Jobs and Benefits Offices throughout Northern Ireland offer a range of free services to help employers find suitable staff and will assist with placing job advertisements both locally and in other countries.
Find your local Jobs and Benefits Office.
You should also ensure advertisements are written in plain English and that the wording, criteria, and images cannot be considered discriminatory.
In addition, you could also run recruitment information sessions to assist potential employees with completing applications and providing monitoring information.
You could also make sure your website is user-friendly for migrant workers by translating the job vacancy section.
You could consider alternative recruitment methods such as roadshows, open days, or even virtual job fairs to actively recruit in other countries.
Recruitment and selection
When carrying out interviews or selection testing:
- consider language issues eg abbreviations that are only understood locally
- make sure your recruitment process schedule allows time to make appropriate travel arrangements
When assessing qualifications and references, you should develop a procedure for qualification equivalency checking. See get your EU professional qualification recognised in the UK.
You could use an organisation such as the European Qualifications Framework or UK ENIC, the designated UK national agency for the recognition and comparison of international qualifications and skills, to assist with evaluating the comparative value of qualifications gained overseas.
ActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/recruiting-migrant-workers
Links
Taking migrant workers through their induction
When taking a migrant worker through their induction, you should remember that they may require additional support.
A new immigration system applies to people arriving in the UK from 1 January 2021. EU citizens moving to the UK to work will need to get a visa in advance. Employers need a sponsor licence to hire most workers from outside the UK.
Please note: this requirement excludes Irish citizens and those who already have settled or pre-settled status under the EU Settlement Scheme.
See right to work checks: employing EU, EEA and Swiss citizens.
When carrying out an induction with a migrant worker, you should remember that they may need additional support.
Beginning employment in a new organisation can be difficult for anyone but working in a new country can bring additional challenges.
Effectively assisting new employees should mean that they adapt more easily to their new roles and become more productive.
Planning an induction
When planning an induction, take into account if the individual's first language is not English.
You should also be sensitive to cultural or religious customs and make sure the process is not discriminatory in any way.
Putting together a welcome pack is a good way to provide key information about your business, employment documents, and facilities. See new starter pack for staff.
It may be useful to include information about living in Northern Ireland and English language classes in the pack. See tailoring the induction to the worker.
Further help following the induction
Following up with new employees after an induction can give you the opportunity to help further with their integration or any queries they may have eg accommodation, childcare, or banking issues.
It may also be useful to link them up with another employee who could act as a 'mentor' and provide further information and support about the business and the local area.
ActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/taking-migrant-workers-through-their-induction
Links
How to support migrant workers in your business
There are many ways you can support migrant workers in your business including having the correct policies and providing appropriate training.
A new immigration system applies to people arriving in the UK from 1 January 2021. EU citizens moving to the UK to work will need to get a visa in advance. Employers need a sponsor licence to hire most workers from outside the UK.
Please note: this requirement excludes Irish citizens and those who already have settled or pre-settled status under the EU Settlement Scheme.
See right to work checks: employing EU, EEA, and Swiss citizens.
Migrant workers may face a number of unique challenges in the workplace, including communication or language barriers, cultural differences or their international qualifications not being recognised in Northern Ireland. As an employer, you should be aware of these challenges and identify ways in which you can support any migrant workers you may employ.
Implement policies and procedures
Your policies and procedures should promote equality of opportunity in the workplace, especially your equal opportunities and harassment policies and procedures.
See disciplinary, grievance, bullying and harassment policies.
You should have equality and diversity policies in place and ensure they are followed and understood across the business. See equality and diversity workplace policies.
Encouraging input from staff when creating and reviewing policies can be useful in ensuring that they are implemented throughout the organisation.
Model policy templates
The Equality Commission provides free model policies that are available to download from the Equality Commission's website.
You should also regularly review these policies in relation to relevant issues such as language and religious and cultural needs.
Racial equality plan template
A good way to take practical action to help you implement your policies and procedures in order to benefit migrant workers and members of other racial or ethnic groups is to develop a racial equality action plan. Find further guidance from the Equality Commission on equality plans, including a racial equality plan template that you can download and adapt for your organisation.
Provide equality and diversity training
Providing equality and diversity training for all workers could also help to embed the correct procedures and values into your business. You should also include bullying, harassment, and dignity at work within this training.
Bullying and harassment training specifically for line managers/supervisors would help them spot signs of bullying or harassment and decide on the best way to deal with any issues that may arise.
Line managers should also monitor the effectiveness of staff training and be proactive in addressing any issues that arise eg a worker having difficulty mixing with other staff.
In addition, having a suitable induction process set up for non-UK nationals is essential in helping them to integrate and settle into the business and the new culture.
See taking migrant workers through their induction.
Focus on language and communication
You should ensure migrant workers understand their legal rights and responsibilities, even if this means translating important documents.
You could also use a mentoring system, where less experienced workers are paired with experienced colleagues who speak the same language.
You could also put flexible arrangements in place to allow attendance at courses in 'workplace English' for speakers of other languages. This would help to reduce the need for translation.
English for Speakers of Other Languages (ESOL) classes focus on speaking and listening, reading and writing, vocabulary and punctuation, and grammar. There are courses available at different levels of competence.
You could also help with integration among staff by organising team events where everyone can get involved eg fundraising events.
Provide training and development opportunities
It is good practice to ensure all employees have the opportunity to develop and enhance their skills, both personally and professionally.
See staff training.
ActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/how-support-migrant-workers-your-business
Links
Local support for employers and migrant workers
Support organisations that are available to Northern Ireland employers and migrant workers.
A new immigration system applies to people arriving in the UK from 1 January 2021. EU citizens moving to the UK to work will need to get a visa in advance. Employers need a sponsor licence to hire most workers from outside the UK.
Please note: this requirement excludes Irish citizens and those who already have settled or pre-settled status under the EU Settlement Scheme.
See right to work checks: employing EU, EEA, and Swiss citizens.
There is a variety of support available to both employers and migrant workers in Northern Ireland.
The Careers Service
The Careers Service, within the Department for the Economy (DfE), provides an impartial, all-age service to help with making informed choices about future career paths.
Find out more about the Careers Service.
Qualifications Equivalence Service
The Department for Communities (DfC) provides the Qualifications Equivalence Service if you are a resident in Northern Ireland and need to check your qualifications against UK equivalents. This free service is accessible through your local Jobs and Benefits office or JobCentre.
A member of staff will arrange a check against UK National Recognition Information Centre (NARIC) database on your behalf, and provide you with comparison information and advice on your specific qualifications.
Not resident in Northern Ireland
If you are a non-UK national from a member state within the EU, EEA or Switzerland with professional qualifications and wish to work in Northern Ireland you may be eligible, under the EU Directive on the Mutual Recognition of Professional Qualifications (Directive 2005/36/EC), for automatic or general recognition of your qualifications depending on your profession.
For further details, see are your country's qualifications recognised in the UK?
The UK European Network of Information Centre (UK ENIC)
UK ENIC (formerly UK NARIC) is responsible for providing information and advice on vocational, academic and professional skills qualifications worldwide.
Managed on behalf of the UK Government, it is provided to help people who are looking for a job or wish to undertake further study.
The Department for Business and Trade
Some professions in the UK are regulated. This can mean there is a legal requirement to have certain qualifications or experience. Other professions are regulated by chartered bodies granting a certain status.
The Department for Business and Trade has a tool to help you check which professions are regulated in the UK and find contact details for regulators of those professions.
Equality Commission
The Equality Commission provides practical advice to employer and service providers on how they can manage the equality implications of employing and managing staff.
This includes helping you to develop a practical and flexible framework to assess your current policies in relation to race and migrant workers and using equality indicators to identify gaps in your policies.
In addition, through the employer training programme, employers can also attend training seminars and information sessions on a wide range of equality issues including managing bullying and harassment and recruiting fairly.
Labour Relations Agency
The Labour Relations Agency (LRA) provides an impartial and confidential employment relations service, including advice on good employment practices and assistance with the development and implementation of policies and procedures.
The LRA also helps to resolve workplace disputes through its conciliation, mediation and arbitration services.
In addition, the LRA hosts a free events programme of best practice seminars, workshops and briefings on a broad range of employment issues throughout the year.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/local-support-employers-and-migrant-workers
Links
Employing migrant workers in Northern Ireland
Recruiting and supporting migrant workers - Avondale Foods (video)
Mia McKeown from Lurgan-based business Avondale Foods explains how they recruit, employ, and support migrant workers in their business.
Avondale Foods, based in Lurgan Co. Armagh, is one of the UK's leading manufacturers and suppliers of coleslaw, wet salads, side salads, vegetable accompaniments, soups, sauces, and mayonnaise to retail and food-service customers throughout Britain and Ireland under their Country Kitchen brand name. Their clients include Waitrose, Marks and Spencer, Sainsbury, Tesco and Asda.
Avondale Foods employs a large number of migrant workers who make up around 60% of their workforce. Here, Mia McKeown, the Human Resources Manager, explains how Avondale Foods recruits fairly, highlights how they support their migrant workers, and outlines the legal considerations for employers.
Case StudyMia McKeownContent category
Source URL
/content/recruiting-and-supporting-migrant-workers-avondale-foods-video
Links