Landlords’ responsibilities
Tenancy Deposit Scheme
Landlords are required to protect the tenant's deposit in a scheme.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
If you are a landlord or letting agent in Northern Ireland and take a deposit on a private tenancy on or after 1 April 2013, then you are required to protect the deposit within 28 calendar days of receiving it using either an insurance or custodial-based protection scheme.
From 1 April 2023, you must not ask for or retain a deposit that is more than one month's rent.
You must also provide certain information about which Tenancy Deposit Scheme is protecting it and you must serve this on your tenants within 35 calendar days of receiving the deposit - this is called 'Prescribed Information'.
Three organisations have been appointed by the Northern Ireland Executive to administer the scheme and further information can be found on each of their websites:
Guidance for tenants
Tenants can read full details of how the Tenancy Deposit Scheme works.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/tenancy-deposit-scheme
Links
Registering as a landlord
All landlords in Northern Ireland must register for the Landlord Registration Scheme.
Landlord Registration Scheme
The Landlord Registration Scheme collects and maintains up-to-date and accurate information on landlords and their properties. All landlords with properties in Northern Ireland must be registered with the scheme. The registration lasts for three years.
Who has to register?
All landlords who let properties under private tenancy in Northern Ireland must register for the Landlord Registration Scheme. You must provide accurate and up-to-date information about yourself and your properties. All joint owners of a property that is let need to register separately.
Renewing your registration
The landlord registration certificate is valid for three years after which you must renew your landlord registration.
Register as a landlord or renew your landlord registration.
How much does it cost?
You only pay one fee regardless of the number of properties you own:
- the online registration fee is £70
- the paper/non-electronic based registration fee is £80
Who is exempt from the registration fee?
As a landlord, you are exempt from the registration fee if you have paid to register a house in multiple occupation which is registered under a Houses in Multiple Occupation Registration Scheme.
Penalties
If you do not complete your registration, you will be committing an offence and may be issued with a penalty of between £500 and £2,500.
Read further information on the registering as a landlord.
Information for landlords who use agents
If someone else looks after the day to day management of your property or if the house is sub-let, you, as the landlord, will still have responsibility for and control of the property. Your property will still have to be registered under the Landlord Registration Scheme.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/registering-landlord
Links
Register a house in multiple occupation
Houses rented to 3 or more unrelated people must be registered as an HMO.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
If you rent out a property to 3 or more unrelated people who share the bathroom or toilet and kitchen, you must register it as a house in multiple occupation (HMO). An HMO, also known as a house share, must meet certain requirements and be registered with your local council.
Houses in Multiple Occupation.
Your responsibilities as a landlord
As a landlord of an HMO, you must:
- ensure the property is not overcrowded
- make sure the property is fit for multiple occupants, ie there is enough cooking space and washing facilities
- provide your local council with all the necessary information about your HMO
Fees for HMOs
You'll have to pay a fee for registration and for any future renewals. Registration is usually valid for 5 years, after this time you can make a renewal. The cost is based on the number of occupants at the property; the more occupants there are, the higher the fee will be. HMO advice for landlords.
How to register your HMO
You can register your HMO by contacting your local council. Find contact details of local councils in Northern Ireland.
Fines and penalties
If you breach any of your agreements with your local council, it may result in a fine, including:
- up to £1,000 for failing to provide the information requested
- up to £5,000 for providing false information
- up to £2,500 if found guilty of overcrowding
- up to £5,000 if someone is living in a part of the property that is deemed unfit for occupation (you'll then be charged up to 10% of the fine every day this continues)
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/register-house-multiple-occupation
Links
Certificate of fitness for rental properties
To rent out a property, you must obtain a certificate of fitness from your local council.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
If you want to rent out a property, you may have to apply to your local council for a certificate of fitness. The certificate of fitness shows that a house is suitable for human habitation and allows you to charge rent at market price.
Applying for a certificate of fitness
Contact the Environmental Health Department of your local council to request a fitness inspection. Find local council contact details in Northern Ireland.
A fee of £50 will be charged for the initial inspection. You will have to complete an application form, providing certain information about your property, including when it was built, the number of rooms, and the facilities provided. This fee will not be refunded if it turns out your property does not require a certificate of fitness, so be sure to check your property's particulars against the exemptions above.
The property inspection
The Environmental Health Officer (EHO) who carries out the inspection will assess the property to ensure that it meets the fitness standard and is fit for human habitation. If the property passes the inspection you will receive a certificate of fitness and be free to charge tenants at a market rate.
If your property fails the inspection, you will receive a schedule of work that will bring the property up to standard. Until this work is completed and the property is re-inspected (for a £100 fee), it will become rent-controlled and the Rent Officer for Northern Ireland will restrict how much rent you are allowed to charge.
Who is exempt?
You don't need to apply for a certificate of fitness if:
- the tenancy began before 1 April 2007
- a renovation or houses in multiple occupation (HMO) grant has been paid by the Northern Ireland Housing Executive (NIHE) (this only applies for a period of ten years from the date of the grant)
- the property is registered with NIHE as an HMO, see register a house in multiple occupation
- the property was formerly let under a protected or statutory tenancy where a regulated rent certificate has been issued (this only applies for a period of ten years from the date of issue of the certificate)
Fines and penalties
If you fail to apply for the inspection of a qualifying property within 28 days of a new tenancy being granted, you may be fined up to £2,500.
Content category
Source URL
/content/certificate-fitness-rental-properties
Links
Rental property health and safety
Landlords' health and safety responsibilities when letting property.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
As a landlord, you are responsible for ensuring the safety of your property. Aside from the general requirements needed for a certificate of fitness for rental properties, you must also meet the following safety requirements.
Electrical safety in rental properties
All mains electrical equipment, new or second-hand, that you supply with the accommodation must be safe and adequate for the needs of your tenant. You must meet the requirements of regulations for supplying electrical equipment. Most equipment with CE marking will satisfy the requirement, as long as they remain in good working order.
Electrical safety: advice for landlords.
Furniture safety in rental properties
If you are providing furnished accommodation, all furniture you supply must comply with fire safety regulations. Many domestic fires start with soft furnishings and toxic fumes given off when upholstery material burns can be fatal; regulations exist to reduce this risk.
Gas safety in rental properties
If your property has gas heating or any gas appliances, you are legally required to have the boiler and any gas appliances inspected every year.
The inspection must be carried out by a Gas Safe registered engineer. Gas safety information for landlords.
Carbon Monoxide has no smell, taste or colour, but it is extremely dangerous and can be fatal. If you install a new or replacement fuel-burning appliance, whether it is gas, coal or oil fired you are legally required to install a carbon monoxide detector in the room where the appliance is located.
Fire alarms in rental properties
If you're building a new property to rent out, or converting a new property you'll have to install fire alarms to comply with building regulations. If your property has three or more non-related tenants (an HMO) you are legally required to install a fire alarm. There is no legal requirement for non-HMO properties, however, landlords should install fire alarms to protect any tenants living there. Failing to install a fire alarm could invalidate your insurance policy. Fire safety advice.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/rental-property-health-and-safety
Links
Landlords’ responsibilities
Rules that landlords must follow when letting out property and their obligations to tenants.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
As a landlord, there are some rules you must follow and certain obligations you have to your tenants.
Requirements for smoke, heat and carbon monoxide alarms
New regulations were introduced on Thursday 30 May 2024 to set a minimum standard for smoke, heat and carbon monoxide alarms in private rental properties.
Landlords' responsibilities for alarm units
It is the responsibility of the landlord to:
- install and keep in proper working order sufficient alarms for detecting smoke, heat and carbon monoxide within any property that they rent out to tenants
- repair or replace any alarm that they have been informed of that is faulty
- ensure that any alarm units (smoke, heat & carbon monoxide) that are bought/installed are marked/referenced as being British Standard compliant
- ensure that if any alarms are to be hardwired into the main electrical installation, that work is undertaken by a qualified electrician
- confirm the tenant is satisfied all alarms are in working order on the commencement of any tenancy
- advise tenants that they need to regularly test the alarms according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and to report any faults to the landlord
Read full details on landlords' responsibilities for alarm units in private rental properties.
Compliance dates
Existing tenancies granted before Sunday 1 September 2024 must comply by Sunday 1 December 2024. New tenancies granted on or after Sunday 1 September 2024 must be compliant on the date the new tenancy is granted.
Repairs in rental properties
In the day-to-day maintenance of the property, you are responsible for any repairs to the structure of the property and any furnishings or equipment supplied with the property. The tenant is responsible for any repairs to their belongings or damage that is their fault.
Records landlords must keep
You are obliged to keep the following records:
- a gas safety certificate, for any gas appliances on the property
- an Energy Performance Certificate
- information on the tenancy deposit protection scheme you've chosen to protect the tenant's deposit and some prescribed information relating to the deposit
- an inventory
You are advised to keep the following records:
- a copy of the Tenancy Information Notice supplied to your tenant(s)
- copies of any receipts for cash payments made by your tenant(s)
Communication with tenants
If you are planning any action that will impact your tenants, you should inform them in a timely manner. Let your tenants know in advance of any of the following:
- repairs and improvements to the property
- sale of the property/the property being repossessed
- you or anyone else entering the property (normally you will need the tenant's permission)
It is important that your tenants are able to contact you when a problem arises and that you respond within a reasonable time. Even if your property is managed by an agent, you still must give your name, a correspondence address, and telephone to the tenant in the Tenancy Information Notice.
Deposits for private rental properties
If you take a tenancy deposit for a private tenancy on or after 1 April 2013 you are legally obliged to protect this deposit in an approved scheme. If the deposit was taken before 1 April 2013 it does not need to be placed in a protection scheme, but you should keep it in a separate account, have clear records about when you received the deposit, and give your tenants a receipt. Read more about the Tenancy Deposit Scheme.
From 1 April 2023, you cannot ask for or retain a tenancy deposit of more than one month's rent. See further information on changes to tenancy deposits.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/landlords-responsibilities
Links
Rental property health and safety
Tenancy Deposit Scheme
Landlords are required to protect the tenant's deposit in a scheme.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
If you are a landlord or letting agent in Northern Ireland and take a deposit on a private tenancy on or after 1 April 2013, then you are required to protect the deposit within 28 calendar days of receiving it using either an insurance or custodial-based protection scheme.
From 1 April 2023, you must not ask for or retain a deposit that is more than one month's rent.
You must also provide certain information about which Tenancy Deposit Scheme is protecting it and you must serve this on your tenants within 35 calendar days of receiving the deposit - this is called 'Prescribed Information'.
Three organisations have been appointed by the Northern Ireland Executive to administer the scheme and further information can be found on each of their websites:
Guidance for tenants
Tenants can read full details of how the Tenancy Deposit Scheme works.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/tenancy-deposit-scheme
Links
Registering as a landlord
All landlords in Northern Ireland must register for the Landlord Registration Scheme.
Landlord Registration Scheme
The Landlord Registration Scheme collects and maintains up-to-date and accurate information on landlords and their properties. All landlords with properties in Northern Ireland must be registered with the scheme. The registration lasts for three years.
Who has to register?
All landlords who let properties under private tenancy in Northern Ireland must register for the Landlord Registration Scheme. You must provide accurate and up-to-date information about yourself and your properties. All joint owners of a property that is let need to register separately.
Renewing your registration
The landlord registration certificate is valid for three years after which you must renew your landlord registration.
Register as a landlord or renew your landlord registration.
How much does it cost?
You only pay one fee regardless of the number of properties you own:
- the online registration fee is £70
- the paper/non-electronic based registration fee is £80
Who is exempt from the registration fee?
As a landlord, you are exempt from the registration fee if you have paid to register a house in multiple occupation which is registered under a Houses in Multiple Occupation Registration Scheme.
Penalties
If you do not complete your registration, you will be committing an offence and may be issued with a penalty of between £500 and £2,500.
Read further information on the registering as a landlord.
Information for landlords who use agents
If someone else looks after the day to day management of your property or if the house is sub-let, you, as the landlord, will still have responsibility for and control of the property. Your property will still have to be registered under the Landlord Registration Scheme.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/registering-landlord
Links
Register a house in multiple occupation
Houses rented to 3 or more unrelated people must be registered as an HMO.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
If you rent out a property to 3 or more unrelated people who share the bathroom or toilet and kitchen, you must register it as a house in multiple occupation (HMO). An HMO, also known as a house share, must meet certain requirements and be registered with your local council.
Houses in Multiple Occupation.
Your responsibilities as a landlord
As a landlord of an HMO, you must:
- ensure the property is not overcrowded
- make sure the property is fit for multiple occupants, ie there is enough cooking space and washing facilities
- provide your local council with all the necessary information about your HMO
Fees for HMOs
You'll have to pay a fee for registration and for any future renewals. Registration is usually valid for 5 years, after this time you can make a renewal. The cost is based on the number of occupants at the property; the more occupants there are, the higher the fee will be. HMO advice for landlords.
How to register your HMO
You can register your HMO by contacting your local council. Find contact details of local councils in Northern Ireland.
Fines and penalties
If you breach any of your agreements with your local council, it may result in a fine, including:
- up to £1,000 for failing to provide the information requested
- up to £5,000 for providing false information
- up to £2,500 if found guilty of overcrowding
- up to £5,000 if someone is living in a part of the property that is deemed unfit for occupation (you'll then be charged up to 10% of the fine every day this continues)
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/register-house-multiple-occupation
Links
Certificate of fitness for rental properties
To rent out a property, you must obtain a certificate of fitness from your local council.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
If you want to rent out a property, you may have to apply to your local council for a certificate of fitness. The certificate of fitness shows that a house is suitable for human habitation and allows you to charge rent at market price.
Applying for a certificate of fitness
Contact the Environmental Health Department of your local council to request a fitness inspection. Find local council contact details in Northern Ireland.
A fee of £50 will be charged for the initial inspection. You will have to complete an application form, providing certain information about your property, including when it was built, the number of rooms, and the facilities provided. This fee will not be refunded if it turns out your property does not require a certificate of fitness, so be sure to check your property's particulars against the exemptions above.
The property inspection
The Environmental Health Officer (EHO) who carries out the inspection will assess the property to ensure that it meets the fitness standard and is fit for human habitation. If the property passes the inspection you will receive a certificate of fitness and be free to charge tenants at a market rate.
If your property fails the inspection, you will receive a schedule of work that will bring the property up to standard. Until this work is completed and the property is re-inspected (for a £100 fee), it will become rent-controlled and the Rent Officer for Northern Ireland will restrict how much rent you are allowed to charge.
Who is exempt?
You don't need to apply for a certificate of fitness if:
- the tenancy began before 1 April 2007
- a renovation or houses in multiple occupation (HMO) grant has been paid by the Northern Ireland Housing Executive (NIHE) (this only applies for a period of ten years from the date of the grant)
- the property is registered with NIHE as an HMO, see register a house in multiple occupation
- the property was formerly let under a protected or statutory tenancy where a regulated rent certificate has been issued (this only applies for a period of ten years from the date of issue of the certificate)
Fines and penalties
If you fail to apply for the inspection of a qualifying property within 28 days of a new tenancy being granted, you may be fined up to £2,500.
Content category
Source URL
/content/certificate-fitness-rental-properties
Links
Rental property health and safety
Landlords' health and safety responsibilities when letting property.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
As a landlord, you are responsible for ensuring the safety of your property. Aside from the general requirements needed for a certificate of fitness for rental properties, you must also meet the following safety requirements.
Electrical safety in rental properties
All mains electrical equipment, new or second-hand, that you supply with the accommodation must be safe and adequate for the needs of your tenant. You must meet the requirements of regulations for supplying electrical equipment. Most equipment with CE marking will satisfy the requirement, as long as they remain in good working order.
Electrical safety: advice for landlords.
Furniture safety in rental properties
If you are providing furnished accommodation, all furniture you supply must comply with fire safety regulations. Many domestic fires start with soft furnishings and toxic fumes given off when upholstery material burns can be fatal; regulations exist to reduce this risk.
Gas safety in rental properties
If your property has gas heating or any gas appliances, you are legally required to have the boiler and any gas appliances inspected every year.
The inspection must be carried out by a Gas Safe registered engineer. Gas safety information for landlords.
Carbon Monoxide has no smell, taste or colour, but it is extremely dangerous and can be fatal. If you install a new or replacement fuel-burning appliance, whether it is gas, coal or oil fired you are legally required to install a carbon monoxide detector in the room where the appliance is located.
Fire alarms in rental properties
If you're building a new property to rent out, or converting a new property you'll have to install fire alarms to comply with building regulations. If your property has three or more non-related tenants (an HMO) you are legally required to install a fire alarm. There is no legal requirement for non-HMO properties, however, landlords should install fire alarms to protect any tenants living there. Failing to install a fire alarm could invalidate your insurance policy. Fire safety advice.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/rental-property-health-and-safety
Links
Landlords’ responsibilities
Rules that landlords must follow when letting out property and their obligations to tenants.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
As a landlord, there are some rules you must follow and certain obligations you have to your tenants.
Requirements for smoke, heat and carbon monoxide alarms
New regulations were introduced on Thursday 30 May 2024 to set a minimum standard for smoke, heat and carbon monoxide alarms in private rental properties.
Landlords' responsibilities for alarm units
It is the responsibility of the landlord to:
- install and keep in proper working order sufficient alarms for detecting smoke, heat and carbon monoxide within any property that they rent out to tenants
- repair or replace any alarm that they have been informed of that is faulty
- ensure that any alarm units (smoke, heat & carbon monoxide) that are bought/installed are marked/referenced as being British Standard compliant
- ensure that if any alarms are to be hardwired into the main electrical installation, that work is undertaken by a qualified electrician
- confirm the tenant is satisfied all alarms are in working order on the commencement of any tenancy
- advise tenants that they need to regularly test the alarms according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and to report any faults to the landlord
Read full details on landlords' responsibilities for alarm units in private rental properties.
Compliance dates
Existing tenancies granted before Sunday 1 September 2024 must comply by Sunday 1 December 2024. New tenancies granted on or after Sunday 1 September 2024 must be compliant on the date the new tenancy is granted.
Repairs in rental properties
In the day-to-day maintenance of the property, you are responsible for any repairs to the structure of the property and any furnishings or equipment supplied with the property. The tenant is responsible for any repairs to their belongings or damage that is their fault.
Records landlords must keep
You are obliged to keep the following records:
- a gas safety certificate, for any gas appliances on the property
- an Energy Performance Certificate
- information on the tenancy deposit protection scheme you've chosen to protect the tenant's deposit and some prescribed information relating to the deposit
- an inventory
You are advised to keep the following records:
- a copy of the Tenancy Information Notice supplied to your tenant(s)
- copies of any receipts for cash payments made by your tenant(s)
Communication with tenants
If you are planning any action that will impact your tenants, you should inform them in a timely manner. Let your tenants know in advance of any of the following:
- repairs and improvements to the property
- sale of the property/the property being repossessed
- you or anyone else entering the property (normally you will need the tenant's permission)
It is important that your tenants are able to contact you when a problem arises and that you respond within a reasonable time. Even if your property is managed by an agent, you still must give your name, a correspondence address, and telephone to the tenant in the Tenancy Information Notice.
Deposits for private rental properties
If you take a tenancy deposit for a private tenancy on or after 1 April 2013 you are legally obliged to protect this deposit in an approved scheme. If the deposit was taken before 1 April 2013 it does not need to be placed in a protection scheme, but you should keep it in a separate account, have clear records about when you received the deposit, and give your tenants a receipt. Read more about the Tenancy Deposit Scheme.
From 1 April 2023, you cannot ask for or retain a tenancy deposit of more than one month's rent. See further information on changes to tenancy deposits.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/landlords-responsibilities
Links
Certificate of fitness for rental properties
Tenancy Deposit Scheme
Landlords are required to protect the tenant's deposit in a scheme.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
If you are a landlord or letting agent in Northern Ireland and take a deposit on a private tenancy on or after 1 April 2013, then you are required to protect the deposit within 28 calendar days of receiving it using either an insurance or custodial-based protection scheme.
From 1 April 2023, you must not ask for or retain a deposit that is more than one month's rent.
You must also provide certain information about which Tenancy Deposit Scheme is protecting it and you must serve this on your tenants within 35 calendar days of receiving the deposit - this is called 'Prescribed Information'.
Three organisations have been appointed by the Northern Ireland Executive to administer the scheme and further information can be found on each of their websites:
Guidance for tenants
Tenants can read full details of how the Tenancy Deposit Scheme works.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/tenancy-deposit-scheme
Links
Registering as a landlord
All landlords in Northern Ireland must register for the Landlord Registration Scheme.
Landlord Registration Scheme
The Landlord Registration Scheme collects and maintains up-to-date and accurate information on landlords and their properties. All landlords with properties in Northern Ireland must be registered with the scheme. The registration lasts for three years.
Who has to register?
All landlords who let properties under private tenancy in Northern Ireland must register for the Landlord Registration Scheme. You must provide accurate and up-to-date information about yourself and your properties. All joint owners of a property that is let need to register separately.
Renewing your registration
The landlord registration certificate is valid for three years after which you must renew your landlord registration.
Register as a landlord or renew your landlord registration.
How much does it cost?
You only pay one fee regardless of the number of properties you own:
- the online registration fee is £70
- the paper/non-electronic based registration fee is £80
Who is exempt from the registration fee?
As a landlord, you are exempt from the registration fee if you have paid to register a house in multiple occupation which is registered under a Houses in Multiple Occupation Registration Scheme.
Penalties
If you do not complete your registration, you will be committing an offence and may be issued with a penalty of between £500 and £2,500.
Read further information on the registering as a landlord.
Information for landlords who use agents
If someone else looks after the day to day management of your property or if the house is sub-let, you, as the landlord, will still have responsibility for and control of the property. Your property will still have to be registered under the Landlord Registration Scheme.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/registering-landlord
Links
Register a house in multiple occupation
Houses rented to 3 or more unrelated people must be registered as an HMO.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
If you rent out a property to 3 or more unrelated people who share the bathroom or toilet and kitchen, you must register it as a house in multiple occupation (HMO). An HMO, also known as a house share, must meet certain requirements and be registered with your local council.
Houses in Multiple Occupation.
Your responsibilities as a landlord
As a landlord of an HMO, you must:
- ensure the property is not overcrowded
- make sure the property is fit for multiple occupants, ie there is enough cooking space and washing facilities
- provide your local council with all the necessary information about your HMO
Fees for HMOs
You'll have to pay a fee for registration and for any future renewals. Registration is usually valid for 5 years, after this time you can make a renewal. The cost is based on the number of occupants at the property; the more occupants there are, the higher the fee will be. HMO advice for landlords.
How to register your HMO
You can register your HMO by contacting your local council. Find contact details of local councils in Northern Ireland.
Fines and penalties
If you breach any of your agreements with your local council, it may result in a fine, including:
- up to £1,000 for failing to provide the information requested
- up to £5,000 for providing false information
- up to £2,500 if found guilty of overcrowding
- up to £5,000 if someone is living in a part of the property that is deemed unfit for occupation (you'll then be charged up to 10% of the fine every day this continues)
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/register-house-multiple-occupation
Links
Certificate of fitness for rental properties
To rent out a property, you must obtain a certificate of fitness from your local council.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
If you want to rent out a property, you may have to apply to your local council for a certificate of fitness. The certificate of fitness shows that a house is suitable for human habitation and allows you to charge rent at market price.
Applying for a certificate of fitness
Contact the Environmental Health Department of your local council to request a fitness inspection. Find local council contact details in Northern Ireland.
A fee of £50 will be charged for the initial inspection. You will have to complete an application form, providing certain information about your property, including when it was built, the number of rooms, and the facilities provided. This fee will not be refunded if it turns out your property does not require a certificate of fitness, so be sure to check your property's particulars against the exemptions above.
The property inspection
The Environmental Health Officer (EHO) who carries out the inspection will assess the property to ensure that it meets the fitness standard and is fit for human habitation. If the property passes the inspection you will receive a certificate of fitness and be free to charge tenants at a market rate.
If your property fails the inspection, you will receive a schedule of work that will bring the property up to standard. Until this work is completed and the property is re-inspected (for a £100 fee), it will become rent-controlled and the Rent Officer for Northern Ireland will restrict how much rent you are allowed to charge.
Who is exempt?
You don't need to apply for a certificate of fitness if:
- the tenancy began before 1 April 2007
- a renovation or houses in multiple occupation (HMO) grant has been paid by the Northern Ireland Housing Executive (NIHE) (this only applies for a period of ten years from the date of the grant)
- the property is registered with NIHE as an HMO, see register a house in multiple occupation
- the property was formerly let under a protected or statutory tenancy where a regulated rent certificate has been issued (this only applies for a period of ten years from the date of issue of the certificate)
Fines and penalties
If you fail to apply for the inspection of a qualifying property within 28 days of a new tenancy being granted, you may be fined up to £2,500.
Content category
Source URL
/content/certificate-fitness-rental-properties
Links
Rental property health and safety
Landlords' health and safety responsibilities when letting property.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
As a landlord, you are responsible for ensuring the safety of your property. Aside from the general requirements needed for a certificate of fitness for rental properties, you must also meet the following safety requirements.
Electrical safety in rental properties
All mains electrical equipment, new or second-hand, that you supply with the accommodation must be safe and adequate for the needs of your tenant. You must meet the requirements of regulations for supplying electrical equipment. Most equipment with CE marking will satisfy the requirement, as long as they remain in good working order.
Electrical safety: advice for landlords.
Furniture safety in rental properties
If you are providing furnished accommodation, all furniture you supply must comply with fire safety regulations. Many domestic fires start with soft furnishings and toxic fumes given off when upholstery material burns can be fatal; regulations exist to reduce this risk.
Gas safety in rental properties
If your property has gas heating or any gas appliances, you are legally required to have the boiler and any gas appliances inspected every year.
The inspection must be carried out by a Gas Safe registered engineer. Gas safety information for landlords.
Carbon Monoxide has no smell, taste or colour, but it is extremely dangerous and can be fatal. If you install a new or replacement fuel-burning appliance, whether it is gas, coal or oil fired you are legally required to install a carbon monoxide detector in the room where the appliance is located.
Fire alarms in rental properties
If you're building a new property to rent out, or converting a new property you'll have to install fire alarms to comply with building regulations. If your property has three or more non-related tenants (an HMO) you are legally required to install a fire alarm. There is no legal requirement for non-HMO properties, however, landlords should install fire alarms to protect any tenants living there. Failing to install a fire alarm could invalidate your insurance policy. Fire safety advice.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/rental-property-health-and-safety
Links
Landlords’ responsibilities
Rules that landlords must follow when letting out property and their obligations to tenants.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
As a landlord, there are some rules you must follow and certain obligations you have to your tenants.
Requirements for smoke, heat and carbon monoxide alarms
New regulations were introduced on Thursday 30 May 2024 to set a minimum standard for smoke, heat and carbon monoxide alarms in private rental properties.
Landlords' responsibilities for alarm units
It is the responsibility of the landlord to:
- install and keep in proper working order sufficient alarms for detecting smoke, heat and carbon monoxide within any property that they rent out to tenants
- repair or replace any alarm that they have been informed of that is faulty
- ensure that any alarm units (smoke, heat & carbon monoxide) that are bought/installed are marked/referenced as being British Standard compliant
- ensure that if any alarms are to be hardwired into the main electrical installation, that work is undertaken by a qualified electrician
- confirm the tenant is satisfied all alarms are in working order on the commencement of any tenancy
- advise tenants that they need to regularly test the alarms according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and to report any faults to the landlord
Read full details on landlords' responsibilities for alarm units in private rental properties.
Compliance dates
Existing tenancies granted before Sunday 1 September 2024 must comply by Sunday 1 December 2024. New tenancies granted on or after Sunday 1 September 2024 must be compliant on the date the new tenancy is granted.
Repairs in rental properties
In the day-to-day maintenance of the property, you are responsible for any repairs to the structure of the property and any furnishings or equipment supplied with the property. The tenant is responsible for any repairs to their belongings or damage that is their fault.
Records landlords must keep
You are obliged to keep the following records:
- a gas safety certificate, for any gas appliances on the property
- an Energy Performance Certificate
- information on the tenancy deposit protection scheme you've chosen to protect the tenant's deposit and some prescribed information relating to the deposit
- an inventory
You are advised to keep the following records:
- a copy of the Tenancy Information Notice supplied to your tenant(s)
- copies of any receipts for cash payments made by your tenant(s)
Communication with tenants
If you are planning any action that will impact your tenants, you should inform them in a timely manner. Let your tenants know in advance of any of the following:
- repairs and improvements to the property
- sale of the property/the property being repossessed
- you or anyone else entering the property (normally you will need the tenant's permission)
It is important that your tenants are able to contact you when a problem arises and that you respond within a reasonable time. Even if your property is managed by an agent, you still must give your name, a correspondence address, and telephone to the tenant in the Tenancy Information Notice.
Deposits for private rental properties
If you take a tenancy deposit for a private tenancy on or after 1 April 2013 you are legally obliged to protect this deposit in an approved scheme. If the deposit was taken before 1 April 2013 it does not need to be placed in a protection scheme, but you should keep it in a separate account, have clear records about when you received the deposit, and give your tenants a receipt. Read more about the Tenancy Deposit Scheme.
From 1 April 2023, you cannot ask for or retain a tenancy deposit of more than one month's rent. See further information on changes to tenancy deposits.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/landlords-responsibilities
Links
Register a house in multiple occupation
Tenancy Deposit Scheme
Landlords are required to protect the tenant's deposit in a scheme.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
If you are a landlord or letting agent in Northern Ireland and take a deposit on a private tenancy on or after 1 April 2013, then you are required to protect the deposit within 28 calendar days of receiving it using either an insurance or custodial-based protection scheme.
From 1 April 2023, you must not ask for or retain a deposit that is more than one month's rent.
You must also provide certain information about which Tenancy Deposit Scheme is protecting it and you must serve this on your tenants within 35 calendar days of receiving the deposit - this is called 'Prescribed Information'.
Three organisations have been appointed by the Northern Ireland Executive to administer the scheme and further information can be found on each of their websites:
Guidance for tenants
Tenants can read full details of how the Tenancy Deposit Scheme works.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/tenancy-deposit-scheme
Links
Registering as a landlord
All landlords in Northern Ireland must register for the Landlord Registration Scheme.
Landlord Registration Scheme
The Landlord Registration Scheme collects and maintains up-to-date and accurate information on landlords and their properties. All landlords with properties in Northern Ireland must be registered with the scheme. The registration lasts for three years.
Who has to register?
All landlords who let properties under private tenancy in Northern Ireland must register for the Landlord Registration Scheme. You must provide accurate and up-to-date information about yourself and your properties. All joint owners of a property that is let need to register separately.
Renewing your registration
The landlord registration certificate is valid for three years after which you must renew your landlord registration.
Register as a landlord or renew your landlord registration.
How much does it cost?
You only pay one fee regardless of the number of properties you own:
- the online registration fee is £70
- the paper/non-electronic based registration fee is £80
Who is exempt from the registration fee?
As a landlord, you are exempt from the registration fee if you have paid to register a house in multiple occupation which is registered under a Houses in Multiple Occupation Registration Scheme.
Penalties
If you do not complete your registration, you will be committing an offence and may be issued with a penalty of between £500 and £2,500.
Read further information on the registering as a landlord.
Information for landlords who use agents
If someone else looks after the day to day management of your property or if the house is sub-let, you, as the landlord, will still have responsibility for and control of the property. Your property will still have to be registered under the Landlord Registration Scheme.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/registering-landlord
Links
Register a house in multiple occupation
Houses rented to 3 or more unrelated people must be registered as an HMO.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
If you rent out a property to 3 or more unrelated people who share the bathroom or toilet and kitchen, you must register it as a house in multiple occupation (HMO). An HMO, also known as a house share, must meet certain requirements and be registered with your local council.
Houses in Multiple Occupation.
Your responsibilities as a landlord
As a landlord of an HMO, you must:
- ensure the property is not overcrowded
- make sure the property is fit for multiple occupants, ie there is enough cooking space and washing facilities
- provide your local council with all the necessary information about your HMO
Fees for HMOs
You'll have to pay a fee for registration and for any future renewals. Registration is usually valid for 5 years, after this time you can make a renewal. The cost is based on the number of occupants at the property; the more occupants there are, the higher the fee will be. HMO advice for landlords.
How to register your HMO
You can register your HMO by contacting your local council. Find contact details of local councils in Northern Ireland.
Fines and penalties
If you breach any of your agreements with your local council, it may result in a fine, including:
- up to £1,000 for failing to provide the information requested
- up to £5,000 for providing false information
- up to £2,500 if found guilty of overcrowding
- up to £5,000 if someone is living in a part of the property that is deemed unfit for occupation (you'll then be charged up to 10% of the fine every day this continues)
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/register-house-multiple-occupation
Links
Certificate of fitness for rental properties
To rent out a property, you must obtain a certificate of fitness from your local council.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
If you want to rent out a property, you may have to apply to your local council for a certificate of fitness. The certificate of fitness shows that a house is suitable for human habitation and allows you to charge rent at market price.
Applying for a certificate of fitness
Contact the Environmental Health Department of your local council to request a fitness inspection. Find local council contact details in Northern Ireland.
A fee of £50 will be charged for the initial inspection. You will have to complete an application form, providing certain information about your property, including when it was built, the number of rooms, and the facilities provided. This fee will not be refunded if it turns out your property does not require a certificate of fitness, so be sure to check your property's particulars against the exemptions above.
The property inspection
The Environmental Health Officer (EHO) who carries out the inspection will assess the property to ensure that it meets the fitness standard and is fit for human habitation. If the property passes the inspection you will receive a certificate of fitness and be free to charge tenants at a market rate.
If your property fails the inspection, you will receive a schedule of work that will bring the property up to standard. Until this work is completed and the property is re-inspected (for a £100 fee), it will become rent-controlled and the Rent Officer for Northern Ireland will restrict how much rent you are allowed to charge.
Who is exempt?
You don't need to apply for a certificate of fitness if:
- the tenancy began before 1 April 2007
- a renovation or houses in multiple occupation (HMO) grant has been paid by the Northern Ireland Housing Executive (NIHE) (this only applies for a period of ten years from the date of the grant)
- the property is registered with NIHE as an HMO, see register a house in multiple occupation
- the property was formerly let under a protected or statutory tenancy where a regulated rent certificate has been issued (this only applies for a period of ten years from the date of issue of the certificate)
Fines and penalties
If you fail to apply for the inspection of a qualifying property within 28 days of a new tenancy being granted, you may be fined up to £2,500.
Content category
Source URL
/content/certificate-fitness-rental-properties
Links
Rental property health and safety
Landlords' health and safety responsibilities when letting property.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
As a landlord, you are responsible for ensuring the safety of your property. Aside from the general requirements needed for a certificate of fitness for rental properties, you must also meet the following safety requirements.
Electrical safety in rental properties
All mains electrical equipment, new or second-hand, that you supply with the accommodation must be safe and adequate for the needs of your tenant. You must meet the requirements of regulations for supplying electrical equipment. Most equipment with CE marking will satisfy the requirement, as long as they remain in good working order.
Electrical safety: advice for landlords.
Furniture safety in rental properties
If you are providing furnished accommodation, all furniture you supply must comply with fire safety regulations. Many domestic fires start with soft furnishings and toxic fumes given off when upholstery material burns can be fatal; regulations exist to reduce this risk.
Gas safety in rental properties
If your property has gas heating or any gas appliances, you are legally required to have the boiler and any gas appliances inspected every year.
The inspection must be carried out by a Gas Safe registered engineer. Gas safety information for landlords.
Carbon Monoxide has no smell, taste or colour, but it is extremely dangerous and can be fatal. If you install a new or replacement fuel-burning appliance, whether it is gas, coal or oil fired you are legally required to install a carbon monoxide detector in the room where the appliance is located.
Fire alarms in rental properties
If you're building a new property to rent out, or converting a new property you'll have to install fire alarms to comply with building regulations. If your property has three or more non-related tenants (an HMO) you are legally required to install a fire alarm. There is no legal requirement for non-HMO properties, however, landlords should install fire alarms to protect any tenants living there. Failing to install a fire alarm could invalidate your insurance policy. Fire safety advice.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/rental-property-health-and-safety
Links
Landlords’ responsibilities
Rules that landlords must follow when letting out property and their obligations to tenants.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
As a landlord, there are some rules you must follow and certain obligations you have to your tenants.
Requirements for smoke, heat and carbon monoxide alarms
New regulations were introduced on Thursday 30 May 2024 to set a minimum standard for smoke, heat and carbon monoxide alarms in private rental properties.
Landlords' responsibilities for alarm units
It is the responsibility of the landlord to:
- install and keep in proper working order sufficient alarms for detecting smoke, heat and carbon monoxide within any property that they rent out to tenants
- repair or replace any alarm that they have been informed of that is faulty
- ensure that any alarm units (smoke, heat & carbon monoxide) that are bought/installed are marked/referenced as being British Standard compliant
- ensure that if any alarms are to be hardwired into the main electrical installation, that work is undertaken by a qualified electrician
- confirm the tenant is satisfied all alarms are in working order on the commencement of any tenancy
- advise tenants that they need to regularly test the alarms according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and to report any faults to the landlord
Read full details on landlords' responsibilities for alarm units in private rental properties.
Compliance dates
Existing tenancies granted before Sunday 1 September 2024 must comply by Sunday 1 December 2024. New tenancies granted on or after Sunday 1 September 2024 must be compliant on the date the new tenancy is granted.
Repairs in rental properties
In the day-to-day maintenance of the property, you are responsible for any repairs to the structure of the property and any furnishings or equipment supplied with the property. The tenant is responsible for any repairs to their belongings or damage that is their fault.
Records landlords must keep
You are obliged to keep the following records:
- a gas safety certificate, for any gas appliances on the property
- an Energy Performance Certificate
- information on the tenancy deposit protection scheme you've chosen to protect the tenant's deposit and some prescribed information relating to the deposit
- an inventory
You are advised to keep the following records:
- a copy of the Tenancy Information Notice supplied to your tenant(s)
- copies of any receipts for cash payments made by your tenant(s)
Communication with tenants
If you are planning any action that will impact your tenants, you should inform them in a timely manner. Let your tenants know in advance of any of the following:
- repairs and improvements to the property
- sale of the property/the property being repossessed
- you or anyone else entering the property (normally you will need the tenant's permission)
It is important that your tenants are able to contact you when a problem arises and that you respond within a reasonable time. Even if your property is managed by an agent, you still must give your name, a correspondence address, and telephone to the tenant in the Tenancy Information Notice.
Deposits for private rental properties
If you take a tenancy deposit for a private tenancy on or after 1 April 2013 you are legally obliged to protect this deposit in an approved scheme. If the deposit was taken before 1 April 2013 it does not need to be placed in a protection scheme, but you should keep it in a separate account, have clear records about when you received the deposit, and give your tenants a receipt. Read more about the Tenancy Deposit Scheme.
From 1 April 2023, you cannot ask for or retain a tenancy deposit of more than one month's rent. See further information on changes to tenancy deposits.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/landlords-responsibilities
Links
Making our services accessible to disabled people - Lyric Theatre (video)
In this guide:
- Disabled access and facilities in business premises
- When a person is considered to have a disability
- How to improve access for people with disabilities
- Accessibility: providing auxiliary aids or services
- Removing physical barriers to access
- Improve access and use of facilities for disabled employees
- Seeking permission when improving access to business premises
- Making our services accessible to disabled people - Lyric Theatre (video)
When a person is considered to have a disability
Description of those people who are legally defined as disabled under the Disability Discrimination Act 1995.
In general, a person is considered to have a disability for the purposes of the Disability Discrimination Act 1995 if they have a physical or mental impairment, which has a substantial, long-term and adverse effect on their ability to carry out normal day-to-day activities.
The Disability Discrimination Act bans disability discrimination by service providers against service-users with disabilities. The law gives people with disabilities important rights on access to everyday services. It also protects the disabled from discrimination by employers against job seekers and employees with disabilities.
See how to improve access for disabled people.
Defining disability
Impairments
Impairments include:
- physical, eg mobility impairments
- mental, eg learning disabilities and some mental illnesses if severe and long term
- sensory, eg hearing impairments or visual impairments
Substantial
Substantial means more than minor or trivial.
Long-term condition
Long-term means the impairment has lasted, or is likely to last:
- for at least 12 months
- for the rest of the life of that person
Activities
Normal day-to-day activities means activities carried out by most people on a regular and frequent basis.
What is not legally deemed a disability?
Conditions not considered to be a disability for the purposes of the Disability Discrimination Act include:
- addiction to alcohol, cigarettes or other drugs - unless they result from drugs that have been prescribed by a doctor
- seasonal allergic rhinitis (including hay fever)
- a tendency to start fires
- a tendency to steal
- a tendency to physically or sexually abuse other people
- exhibitionism
- voyeurism
ActionsAlso on this siteMore Case StudiesContent category
Source URL
/content/when-person-considered-have-disability
Links
How to improve access for people with disabilities
Change policies and procedures to improve disabled people's access to your business premises, products, and services.
Your business will have established a way of providing a service to your customers. This involves establishing:
- practices - what your business actually does
- policies - how your business regulates what it does
- procedures - the systems set up to ensure the policies are achieved
Formal and informal practices on access
Practices, policies, and procedures may be:
- set out formally, eg a ban on animals entering the premises
- established informally or by custom, eg owners are discouraged from entering the premises with an animal but there is no outright ban or penalty for non-compliance
Accessibility audit
It is good practice to carry out an accessibility audit of your business. This will identify areas where you could make it easier for disabled people to access your business and its services. The Equality Commission provides an accessible business checklist (PDF, 581K) as part of their every customer counts initiative to help businesses assess and improve their accessibility.
Understand your customers
Good business involves anticipating what your customers need and want including the needs of disabled customers. Talk to your customers about the issues they may have when using your services, such as parking, getting in and out of your premises or using the facilities. Ask them for recommendations on how you could improve accessibility.
It is a good idea to think about the range of impairments that your customers may have, such as:
- mobility impairments eg stick users or wheelchair users
- visual impairments
- hearing impairments
- arthritis and limited dexterity
- mental health
- learning difficulties
- learning disabilities
This will give you a better understanding of potential barriers to access for some of your customers. This enables you to take steps to remove these barriers.
Making reasonable adjustments for disabled access
Your business may have in place certain practices, policies and procedures which may place people with a disability at a disadvantage compared to non-disabled people in accessing your goods or services. You must make reasonable adjustments that let you provide a service that is as close as possible to the standard of service provided to other people. You must not wait until a disabled person wants to use a service before making any reasonable adjustments.
You must consider the need for, and put in place, any reasonable adjustments required by customers with a disability.
You can do this by:
- removing the practice, policy or procedure altogether
- making exceptions to the practice, policy or procedure to accommodate disabled people
- informing, instructing, and training all employees so that they are aware of these changes
Examples of changing practices to improve disability access
Examples of changing practices, policies, and procedures include:
- waiving a 'no dogs' policy to allow disabled people accompanied by an assistance dog to enter your premises
- allowing other forms of identification other than a driving licence - thereby allowing disabled people who are not permitted to hold a driving licence to access your goods or services
Accessibility guides for businesses
You can download the following accessibility guides from the Equality Commission:
Also on this siteMore Case StudiesContent category
Source URL
/content/how-improve-access-people-disabilities
Links
Accessibility: providing auxiliary aids or services
Use equipment, technology, and extra services to help disabled people access what you offer.
An auxiliary aid is a piece of equipment or technology that can help a person with a disability access your goods or services. An example would be an induction loop for people with hearing impairments. Auxiliary aids are not limited to communication, for example, you might provide a portable ramp or handrails to help customers with mobility impairments.
Auxiliary service
An auxiliary service means providing assistance to help a person with a disability to use your goods or services.
Examples of such auxiliary services include:
- training a member of staff in British Sign Language (BSL) or Irish Sign Language (ISL) so that they are able to communicate effectively with customers who have a hearing impairment and who use BSL as their main form of communication - see communication support for deaf people
- helping a customer in a wheelchair to access goods that are out of their reach or bringing goods to the till if aisles cannot be accessed by wheelchair users
When considering what auxiliary aids or services are required, you will need to take into account that different people will have different requirements. Some people, for example, may have multiple disabilities, such as speech and hearing impairments.
Judging whether the aids and services are reasonable
You should take reasonable steps to provide auxiliary aids and services. What is regarded as 'reasonable' for one business may be different for another business. Whether the auxiliary aids and services you provide are judged as reasonable may depend on such things as:
- the size of your business
- the resources available to your business
- the cost of providing the extra aid or service
In the event of a dispute, only a court can decide what is reasonable.
For further information see reasonable adjustment - Equality Commission's guidance.
Making permanent alterations to your business premises
You may be required to make reasonable adjustments to the physical features of your business property to ensure your services are accessible to disabled people. See removing physical barriers to access.
ActionsAlso on this siteMore Case StudiesContent category
Source URL
/content/accessibility-providing-auxiliary-aids-or-services
Links
Removing physical barriers to access
How to provide access to your services and products for people with disabilities.
The physical features of your business premises can create barriers that can put people with a disability at a substantial disadvantage compared to non-disabled people when accessing your goods or services.
Definition of a physical feature
A physical feature:
- is determined by the design or construction of the building
- forms part of the approach, entrance, or exit to your property
- can be fittings, fixtures, furniture, equipment, machinery, or materials
- is any other physical element on your business premises
Examples of a physical feature
Examples of physical features include:
- steps, stairways, kerbs
- floors and paved areas
- doors and gates
- toilets and washing facilities
- lighting and ventilation
Legal requirements on physical barriers
Under the Disability Discrimination Act you must make reasonable adjustments to ensure those with a disability overcome any potential physical barriers. You can do this by:
- removing the physical feature altogether
- changing it so it no longer creates a physical barrier
- providing a reasonable means of allowing disabled people to avoid using the physical feature
Reasonable adjustments
You are required to make reasonable adjustments to your business premises, to the way you do things or by providing auxiliary aids or services where disabled customers and potential customers may be at a substantial disadvantage compared with non-disabled customers. See disability - what the law says.
See reasonable adjustments - Equality Commission guidance.
Removing barriers created by physical features
Examples of removing barriers created by physical features to help people with a disability access your goods and services include:
Car parking spaces
Providing a wider car parking space in your customer or staff car park reserved for use by Blue Badge holders.
Ramps
Replacing steps with temporary or permanent ramps at the entrance of your premises.
Hand rails
Fitting hand rails to help disabled people use small steps, eg one or two steps.
Doorways
Widening doorways so that wheelchairs can pass through easily.
Signage
Making signs easier to read, eg you could supplement written signs with pictures and visual signs.
Passageways
moving furniture or other obstacles to allow a clear passageway for people with a mobility or visual impairment.
See Disability Action's guidance on reasonable adjustments in the workplace to help make your business premises accessible to everyone.
ActionsAlso on this siteMore Case StudiesContent category
Source URL
/content/removing-physical-barriers-access
Links
Improve access and use of facilities for disabled employees
Make reasonable adjustments to physical features in the workplace to ensure equal access for staff with disabilities.
You may need to make alterations and changes to physical features to accommodate staff with a disability. If the physical feature puts disabled employees at a disadvantage, you must adjust it to remove or reduce the impact of the physical barrier. These alterations are known as reasonable adjustments.
Reasonable adjustments for staff
These steps could include, where reasonable, making structural or physical changes to your business premises, such as:
- widening doorways to allow a wheelchair to pass through easily
- replacing steps with ramps
- relocating light switches and door handles to a level that considers people who have difficulty in reaching
- putting in place audio-visual fire alarms
- providing accessible toilet facilities for disabled employees
These reasonable adjustment steps also involve allowing the person to work in a more easily accessible place, such as by:
- transferring a wheelchair user's workstation from an inaccessible upper floor to the ground floor
- allowing a disabled job applicant to be interviewed in an accessible room
- providing specially modified equipment, such as a special keyboard adapted for someone who has arthritis, or a telephone adapted for someone with a hearing impairment
Employer's legal duties to make reasonable adjustments
If you are an employer, you have duties under the Disability Discrimination Act 1995 not to discriminate against and to make reasonable adjustments for your employees or job applicants with a disability.
The employment provisions of the Disability Discrimination Act apply to all employers, regardless of size, except service in the armed forces.
The reasonable adjustment duties under the employment provisions are not anticipatory and therefore you are only required to consider the needs of an actual disabled employee or, in the case of the recruitment process, a disabled job applicant. Reasonable adjustments in the workplace - Disability Action guidance.
Download the disability code of practice for employers (PDF, 926K).
Do you need to make an adjustment to a physical feature?
You only need to make adjustments to your business premises if a disabled employee would otherwise be at a substantial disadvantage to that of a non-disabled employee. Before making the reasonable adjustment, you could consider:
- the extent to which the disadvantage would be alleviated
- the cost of making the adjustment
- what financial resources your business has access to
- whether you have access to external resources to help you bear the cost
- whether adjustments have been made for other disabled employees
- how willing the disabled employee is to co-operate with any adjustment you make
See reasonable adjustment - Equality Commission guidance.
Advice and support for hiring disabled people
The Access to Work programme provides practical support to disabled people to help overcome barriers in the workplace. It can also provide help to employers.
Workable (NI) provides supported job opportunities for disabled people who face more serious obstacles in obtaining or retaining a job. This helps them access the support they need to work effectively.
ActionsAlso on this siteMore Case StudiesContent category
Source URL
/content/improve-access-and-use-facilities-disabled-employees
Links
Seeking permission when improving access to business premises
The permission you might require when making changes to improve access for disabled people on your business premises.
If you provide services to the public, you are legally required to take reasonable steps to ensure that the physical features of your business premises do not make it unreasonably difficult or impossible for people with disabilities to make use of your service.
Before you make any significant alterations or changes to your property, you should check whether you require planning permission or building regulations approval.
You need to apply for planning permission through your local council.
Making changes to rented premises
If you rent your business property, you usually need to get consent from your landlord before you make any significant alterations to enable disabled people to access and use your premises.
You must request consent for any alterations to accommodate disabled people even if the terms of your lease state that alterations to the property are not allowed. The Disability Discrimination Act allows the terms of the lease to be read to entitle you to make the alteration with the consent of your landlord.
Procedure for requesting consent from your landlord
You should make a written application for consent from your landlord to make alterations to rental properties to allow disabled people to access and use your business premises.
You should also include all plans and specifications with your applications to avoid any possible delays.
Once your landlord has received your application he or she has eight weeks to respond.
Your landlord should not unreasonably withhold consent. But they may set certain conditions that you should carry out before you make any alterations. These include:
- gaining planning permission from your local authority
- carrying out alterations in accordance with plans and specification
- allowing the landlord to inspect the works
- reimbursing, within reason, any costs the landlord may have incurred in giving consent
If your landlord does not respond to your request within eight weeks, you can assume that he or she has withheld consent. You should then refer the matter to the county court.
Similarly, if your landlord refuses to give you consent, or sets other conditions, again, you should refer the matter to the county court. The court will decide whether the landlord is reasonable in refusing consent.
ActionsAlso on this siteMore Case StudiesContent category
Source URL
/content/seeking-permission-when-improving-access-business-premises
Links
Disabled access and facilities in business premises
Making our services accessible to disabled people - Lyric Theatre (video)
This video case study outlines how the Lyric Theatre’s premises, equipment, and services make its facilities accessible for all.
Ciaran McAuley, Chief Operating Officer at the Lyric Theatre, explains how they make their facilities accessible to disabled people.
When the Lyric Theatre was rebuilt in 2011, steps were taken to ensure the new building would be accessible to all. Equipment and services such as audio-described shows and induction loops, make it easier for customers with disabilities to attend performances.
Ciaran explains the approach the Lyric take in regard to accessibility and how they work with staff and customers to continue providing accessible services.
Case StudyCiaran McAuleyContent category
Source URL
/content/making-our-services-accessible-disabled-people-lyric-theatre-video
Links
Choosing the right premises to suit our business needs - Totalmobile (video)
In this guide:
- Choosing business property
- Business property specification
- Choose the right location for your business premises
- Legal considerations when choosing business property
- Deciding on the right premises for your business (video)
- Search for commercial property
- Six tips for choosing the right business property
- Choosing the right premises to suit our business needs - Totalmobile (video)
Business property specification
Preparing a specification that sets out what you want when starting a search for commercial premises.
Drawing up a list of what you need from your business premises is a good way to start your property search. This list is known as a property specification or property spec.
Property specification
Your property spec might list details on how the following requirements should be met when looking for suitable business premises.
Property size and layout
Do you want an open-plan style office space or individual rooms for more privacy? Do you need additional space for equipment, storage, meetings or socialising?
Property appearance
Both internally and externally. For example, do you need a visually attractive property both from the outside as well as the inside especially if clients and/or customers are going to be visiting your business property?
Property structure
Do you require any special structural property requirements such as high ceilings, upper-floor loading or reinforced foundations?
Premises facilities
You should consider the comfort of employees and visitors - including lighting, toilets, reception areas and kitchen facilities.
Property utilities
This can include things such as power and drainage, and any special requirements - for example, three-phase electricity. Take note of the power and heating/cooling requirements that you may need eg power points for computers and heating and air conditioning for staff and customer comfort. An older building may need to be rewired, a new heating or air conditioning system installed or additional toilet and kitchen facilities built. It is also a good idea to identify the broadband capabilities that you will require.
Planning permission
You should take into consideration that you may need to seek planning permission to use the property for your type of business.
Access and parking
Take into consideration access to the property, is it important for it to be near main roads and/or public transport? Is the property accessible for deliveries or customers, including disabled customers? In addition, do you have a requirement for car parking?
Option to extend or make alterations
Consider how flexible the property is so that you are able to make alterations or expand the property if required.
Long-term business plans
Look at your business plan and weigh up how the business property you choose fits into these plans and business direction.
Property location
You also need to think about where you want your property to be located - for detailed location factors you should consider, see choose the right location for your business premises.
Property costs
Your choice of commercial property will also depend on your budget. Whether you rent or buy business premises, costs can include:
- initial purchase costs, including legal costs such as solicitor's fees and professional fees for surveyors
- initial alterations, fitting out and decoration
- any alterations required to meet building, health and safety and fire regulations
- ongoing rent, service and utility charges, including water, electricity and gas
- business rates
- continuing maintenance and repairs
- building and contents insurance
Compare the costs of buying business property with the costs when renting commercial property.
Energy performance of the property
Sellers and landlords are obliged to provide prospective buyers or tenants with an Energy Performance Certificate (EPC). An EPC indicates how energy efficient a building and its services are and can act as a good indicator of likely energy costs. For more information, see Energy Performance Certificates for business properties.
If your property requirements are too specific, you may find that your choice of premises is very limited or you cannot afford them. Think about which requirements are essential and which are desirable, and prioritise them accordingly to make your property decision.
Working from home
After drawing up your list of property requirements, you may decide that working from home could suit you better. However, there are important legal and practical issues you need to take into account - see use your home as a workplace for further guidance.
Also on this siteMore Case StudiesContent category
Source URL
/content/business-property-specification
Links
Choose the right location for your business premises
Identify the advantages and disadvantages when deciding on a suitable location for your commercial property.
A good location for your business is vital, but choosing the right one can be something of a balancing act. Ideally, the location should be convenient for your customers, employees, and suppliers - without being too expensive for your business. You should weigh up the advantages and disadvantages of various locations when deciding on a suitable place for your business property.
Location factors for business property
In order to judge the best location for your business you should consider key location factors and how important each of these are for you and your business priorities. You should consider:
Footfall
Depending on the nature of your business, the amount of passing trade can have a huge impact on the success of your venture especially if your business operates in the retail sector.
Competitors in the area
Although some businesses, like estate agents, can benefit from being located in a cluster of similar businesses, for many others having too many close competitors can have a severe impact on sales and profitability. It is always worthwhile surveying the local area to see if there are potential competitors in the vicinity and considering how this could impact your trade.
Transport links and parking
Good public transport links and local parking facilities make it easier for employees and customers who don't live within walking distance to access your business.
Delivery restrictions
These can cause problems for your suppliers, so you'll need to make sure that your premises are easily accessible if you expect to have regular deliveries.
Planning restrictions
Make sure you check whether you're allowed to use the premises for the commercial purpose you have in mind.
Business rates
These can add greatly to the ongoing costs of locating in a particular area, which may make the premises less desirable from your point of view - see estimate your rate bill to get an idea of what you may have to pay.
Local amenities
Employees generally prefer working in areas with good local facilities, and you may need to make regular trips to the bank or a postal depot.
Type of area
The image of your business may well be affected by the nature of your location and whether crime or anti-social behaviour is .
Making a decision
Whatever option you go for, there are likely to be advantages and disadvantages to the business location that you choose. An office in a rural setting might be relaxing, but could be awkward for staff or suppliers making deliveries to access. Being right in the middle of the city could be very convenient, but might also be expensive in terms of property cost and business rates payable. It may also be costly and inconvenient for car parking within city or town centres.
Location has a major impact on business costs. If you need property in a prime location the extra costs may be justified.
Also on this siteMore Case StudiesContent category
Source URL
/content/choose-right-location-your-business-premises
Links
Legal considerations when choosing business property
Key legal obligations and restrictions to consider when choosing commercial premises.
If you own or occupy a business property, you need to understand the legal obligations and restrictions that may affect you. For example:
- The property must have planning permission that allows it to be used for your type of business.
- You must comply with building, fire, and health and safety regulations. See fire safety and risk assessment.
- Stamp duty is payable on commercial leases and you are likely to be liable for business rates, though in rented premises these may be paid by the landlord.
- You are responsible for the health and safety of employees and visitors. See workplace welfare facilities and healthy working environment.
- You also need to provide a suitable working environment.
- If you provide goods or services to the public, you must take reasonable steps to make your premises accessible. See disabled access and facilities in business premises.
- You need to comply with the terms of any lease or licence agreement. See commercial property: landlord and tenant responsibilities.
- For some businesses, you may require a licence to operate or to sell certain products.
- There may be restrictions on certain periods of time throughout the day or week when deliveries are allowed. There may also be limits on noise and pollution levels that you must meet. You may also have to consider how you or your customers dispose of waste.
- Whatever premises you choose, you need to ensure that you are properly insured. See insurance: business property and assets.
If you are in any doubt about your legal obligations, you should seek professional legal advice from your business adviser or solicitor. Choose a solicitor for your business.
More Case StudiesContent category
Source URL
/content/legal-considerations-when-choosing-business-property
Links
Deciding on the right premises for your business (video)
Short video outlines key factors to consider when deciding on suitable business premises.
Short video (2 minutes 30 seconds) outlines important factors to consider when making decisions about your business premises such as cost, location, facilities and infrastructure.
Also on this siteMore Case StudiesContent categorySelect subtypeVideo
Source URL
/content/deciding-right-premises-your-business-video
Links
Search for commercial property
Specifying what you want when searching for business premises and where you can search for suitable commercial property.
It's worth starting your property search by drawing up a business property specification or 'spec', clearly setting out your business property requirements. This will help distinguish between what is essential and what is desirable in a property for your business. It will also identify the order of priorities when it comes to factors influencing the type and location of the commercial property you desire.
You can then circulate your property specification to estate agents and surveyors that handle commercial properties in your area. They can then let you know if any properties are currently available that match or come close to meeting your requirements.
Searching for commercial property
You can search for business property in Northern Ireland using our commercial property finder.
You may also decide to search for suitable business premises yourself. Commercial property is listed online by estate agents on their own websites or on third-party property listing websites such as PropertyPal, Rightmove, Zoopla, or PrimeLocation, as well as many others.
Check any potential properties against your specification and eliminate any premises that don't at least meet all your essential requirements. Then you can draw up a shortlist of potential business properties to visit.
Professional advice
At this stage, you may want to seek the advice of a surveyor or solicitor. For example, a surveyor can assess the condition of a property and give you an idea of their value. See buying commercial property: using a surveyor.
When you're ready to make an offer or agree the terms of a lease, your solicitor can help negotiate the property deal and complete the legal work. See buying commercial property: using a solicitor.
Also on this siteMore Case StudiesContent category
Source URL
/content/search-commercial-property
Links
Six tips for choosing the right business property
Six tips to help you find a suitable commercial property to buy or rent for your business.
Top tips to help you find suitable commercial premises
1. Draw up a list of what you need from your business premises
How important is property size, layout, location, facilities, structural requirements, and parking to your business needs? Also, think about your long-term business plans and how these might affect your choice of business premises. For example, you might want to expand or alter the property in the future. Order your list by prioritising your desired requirements from the top down. This will help you visualise what the most important factors are for you and your business when deciding on a suitable commercial property. See business property specification.
2. Location, location, location
Choosing the right location for your business premises can be a bit of a balancing act. You may want to choose a location that is convenient for your customers, employees, and suppliers, but isn't too expensive. Some factors you might want to consider when deciding on location include, footfall, where competitors are located, delivery restrictions, parking restrictions, and business rates.
3. Determine whether to buy or rent a business property
You will need to determine whether either buying or renting a commercial property is best for your business needs. You should compare the advantages of renting commercial property with the advantages and disadvantages of buying business property This short video will also help you to weigh up the pros and cons when deciding whether to rent or buy business premises (video).
4. Business rates
Before agreeing to buy or rent a commercial property you will want to get an idea of what you are likely to pay in business rates - estimate your rate bill. You may be eligible for assistance with business rates. See help available for business rates.
5. Legal considerations for commercial property
There are a number of legal considerations when choosing business property including planning permission, health, safety and fire regulations, insurances, accessibility and licences. You will probably need to pay stamp duty if you purchase the property or if you rent a commercial property you will need to comply with the terms of the lease. Ensure you get advice from a solicitor when buying or leasing business premises.
6. Search for commercial property
You can search for commercial property through local commercial property agents, visiting potential areas to see commercial properties for sale or rent, or searching our commercial property finder. Check potential premises against your requirements to create a shortlist of the business properties you might want to view.
Also on this siteMore Case StudiesContent category
Source URL
/content/six-tips-choosing-right-business-property
Links
Choosing business property
Choosing the right premises to suit our business needs - Totalmobile (video)
Video case study explaining how Totalmobile found the right premises to suit the needs of their growing business.
Malcolm Thompson, Chief Operating Officer of software provider Totalmobile, explains how they chose new premises to suit the needs of their growing business.
As Totalmobile expanded and their requirements changed, the business decided to move from its premises in the Antrim Technology Park to new rented premises in Belfast. The business had to consider various factors in order to make the right choice.
Here Malcolm and Chief Executive Colin Reid discuss how the business identified the right premises and overcame the challenges of the move.
Case StudyMalcolm ThompsonContent category
Source URL
/content/choosing-right-premises-suit-our-business-needs-totalmobile-video
Links
Reporting a crime against your business
In this guide:
- Protect your business against crime
- Business security survey
- Secure your business premises
- Business security: protecting staff
- Secure your business assets
- Business security: cash
- Business security: stock and theft prevention
- Reporting a crime against your business
- Preventing identity theft, scams and fraud
- Business security plans and procedures
- CCTV surveillance
Business security survey
How to protect your business internally and externally by performing a survey to reveal weaknesses in security.
To protect your business premises, you should first assess the local environment, eg street, business park or shopping centre. You can look at the level and types of crimes that are being carried out in your area using the Police Service of Northern Ireland's (PSNI's) official crime statistics.
Business security survey
This assessment will form part of your first steps to performing a full security survey. A business security survey should include both an external and an internal assessment of any crime risks to your business. Try the onion-peeling principle, which involves thinking about your business and its premises as a series of layers, to conduct your survey.
Preparation for security survey
When using the onion-peeling principle, you should take security measures at each layer to delay and deter the criminal and to protect or remove any potential targets for crime. There are three types of physical targets in most businesses:
- buildings - eg stores and garages
- property - eg cash, stock and equipment
- people - ie staff, security guards and visitors
Your aim at each layer is to:
- reduce the potential rewards of crime
- reduce any potential provocation to commit crime
- remove any potential excuses for criminal behaviour
You should concentrate on all areas of security and consider all potential targets and the effects on them, such as financial loss, temporary closure, inability to deliver goods, or staff morale. Other risks to consider include: fraud, violence, graffiti, computer data theft, etc.
When preparing your security survey, you should take into account:
- the amount and types of crime in the area
- whether anyone nearby has been a victim of crime
- whether any business crime partnerships exist in the area
Use a map to identify access to your business property and potential entry and escape routes. You need to consider any escape routes for offenders that may not be easily seen.
Carrying out a security survey
Consider using a security checklist when undertaking a safety survey to ensure that you cover all areas of concern.
You should keep notes on your security survey to help future security plans and make them more effective.
There are four areas to consider for your security survey:
Environment
The area around your business - eg the street or alleys bordering your premises.
Perimeter
How someone could gain access to your business property from the public space.
Outer shell
For example, doors and windows that could provide access to your buildings.
Interior
Consider inside the building, and how this could be protected from criminal activities.
You should walk around the boundary of your business property and check for any weak areas, both during the day and when dark. Identify opportunities for crime, such as:
- walls or fences that could be climbed
- bins or other objects that could be used to climb or could be targeted for arson
- tools or materials left out that could be used to break in
- possible hiding places
- any poorly lit areas that could be used as cover for a break-in
Fencing and property boundaries
Steel fencing, railings or walls of at least 2.5 metres in height can make effective boundaries for your business property. You could also use barbed or razor wire, rotating vanes or electric fence alarms at the top of fences or walls, and anti-climb paint to make access harder.
When dealing with the shell, you should think about security measures that will delay an attempted break-in or put off potential offenders.
You should pay particular attention to the:
- roof, especially a flat roof
- cellar
- loading bay
- side of your business
- back of your business
You should think about how a criminal might view the business when open and closed, during the day or at night.
ActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/business-security-survey
Links
Secure your business premises
Secure your business property by applying the right security measures to deter criminals.
In order to protect your business property from crime, first carry out a business premises security survey. Once you have determined the main security risks to your business, you can decide what actions you should take.
Which security measures should I take?
The basic idea is to introduce measures that will delay and deter potential offenders from seeing your business as an easy target for crime. We have outlined below security measures that you could apply to protect your business:
Secure access points
Have strengthened doors fitted, ensure all windows have locks, install strengthened shutters, and ram raid barriers if necessary.
Secure the perimeter
Ensure gates are secure and fences aren't damaged or provide opportunities for access. Applying anti-climb measures can also be effective, however, you must have signs to state you have them installed.
Access control
Control access to the business by keeping a record of who has keys or passes and ensure employees that leave hand them back.
Lighting
Install security lights at dark points that will come on when movement is detected.
Alarms
Fit intruder alarms.
Secure property
Secure equipment with asset tags and record details of serial numbers. You should also consider securing devices such as laptops and tablets to larger equipment such as desks. Secure your business assets.
Stock control
Protect stock by keeping regular tabs on stock levels.
IT security
Address IT security issues such as hard-drive encryption, off-site data storage, and software security updates. Protect your business online.
Sensitive information
Carefully dispose of any sensitive documents or information by shredding sensitive paper waste.
Security cameras
Install CCTV surveillance and regularly check that your cameras are in full working order.
Any measures that you take should be legal, appropriate, realistic and cost-effective.
For further guidance on securing your business property see the National Security Inspectorate's workplace security safety guidance.
Professional security consultants can offer a comprehensive risk assessment of any premises and can recommend security measures to meet the risks faced.
ActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/secure-your-business-premises
Links
Business security: protecting staff
How to provide a safe workplace and develop strategies that will protect employees from criminal and violent behaviour.
As an employer you have a employers' health and safety responsibilities. Bringing in measures to improve staff safety and making employees and customers aware of their responsibilities can also improve the security of your business.
Improve staff security
Steps you can take might include:
- checking visitor and delivery personnel identities
- always checking the identity of people you deliver to
- getting signatures for the receipt and issue of goods
- CCTV system to cover entrances and exits
High security risk businesses
If your business handles a lot of cash or expensive goods, it makes sense to use a properly fitted protective screen to protect staff (eg at a cash register), closed-circuit television (CCTV), and secure storage such as a safe. See business security: cash.
If your business is at risk or is in a high-risk area, it might also be appropriate and cost-effective to employ security guards.
You could also join local community initiatives or Neighbourhood Watch initiatives. Contact the PSNI for details of initiatives in your area.
Customers and business security
All customers should be asked to remove motorcycle helmets and scarves that cover a face before they enter your business premises. A height mark at the door can be used by staff to accurately gauge the height of a criminal if a report of crime needs to be made to the police. If the height mark is highly visible this can also act as a deterrent for potential criminals that target your shop.
Employees who work alone
If you employ staff who work alone, you can help to reduce risks to them by using:
- personal alarms
- radio link scheme
- controlled access or CCTV with audio
- automatic warning devices
- lone-worker monitoring devices
- regular police or security checks
You could also ask staff to vary their routes and times for added security. Ensure lone workers' safety.
When a violent incident happens
Violent incidents can involve theft, angry customers, or customers under the influence of alcohol or drugs. You can offer staff training in conflict management to deal with aggressive customers. Advise staff not to put themselves at risk, and to move away from aggressive customers but avoid becoming isolated.
When necessary they should dial 999 or get help quickly by using an alarm. They should try to write down information about what happened and secure CCTV footage and the scene until the police arrive.
All such incidents should be reported to the police. This can be done by dialling 999 in an emergency, or 101 for non-emergency situations.
Victim support
If a member of staff is a victim of violence, they may need medical attention, which may be available in-house or may be required from the ambulance service. However, they will need your support. This might include:
- a debriefing - talking about what happened
- giving time off to recover
- suggesting specialist counselling
Other staff who witnessed the incident may also be affected. They can get help and support from Victim Support NI.
Download violence at work guide (PDF, 105K).
Bomb threats and suspect packages
You should ensure staff know what to do in the unlikely event of a bomb threat or a suspect package is found on your business premises. Download the PSNI's business guidance on dealing with bomb threat telephone calls and suspect packages (PDF, 212K).
Tiger kidnap
Tiger kidnap involves the short-term hostage-taking of family members of an employee who has immediate access to cash or valuables. The captives are frequently held overnight and the aim of the criminals is to frighten their victims to such a degree that they will not contact the police, even when they have an opportunity to do so.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/business-security-protecting-staff
Links
Secure your business assets
How to identify and protect your assets, including your vehicles and transported goods.
There are a few simple procedures to follow that will help to protect your assets on and off-site. Assets or property could include:
- computer equipment, laptops, or tablets
- mobile phones
- information stored on computers, organisers, or on paper
- business vehicles
- specialist equipment and tools
- plant and machinery
Marking business assets
You should permanently mark each piece of equipment and make a note of the:
- make
- model
- serial number
You should also maintain a record of all business assets, where they are located, and who is responsible for them. Asset checks, as well as stock checks, should be carried out by a dedicated member of staff.
Secure essential and high-value equipment in a separate secure room.
Computer equipment and mobile phones
If a computer, laptop, or tablet is lost or stolen, often the loss of information and data can be more of a serious issue than the cost of a replacement. This will particularly be the case if personal information is held on the computer. It could damage your reputation, affect your business's ability to operate, put individuals at risk, and result in a substantial fine. Read PSNI guidance on what you can do to protect computers in your business.
A way to address this issue would be to use cloud computing. This lets you store business information and use hardware and software remotely and securely over the internet.
Protecting business data
You should carry out an assessment of the risks and take measures to keep your physical and information assets safe. Common threats include:
- cyber crime - malicious people might gain access to your systems and alter, steal or delete data - cyber security risk management
- viruses - programs that are created to cause a nuisance or damage computer systems - detect spam, malware, and virus attacks
- fraud - theft of sensitive data such as employee records or valuable intellectual property by hackers or even your own employees - business data breach and theft
- data loss - caused by any of the above or by loss of hardware - eg by a flood at your premises
Small steps can help increase data security. For example, all computers should be password protected and have an internet firewall and anti-virus software. Employees who use computer equipment on a regular basis should change their passwords and back up their files regularly. Any information kept on electronic equipment should be copied and kept securely off-site and in a fire-proof safe. Protect your business online.
Every individual mobile phone can be identified by a unique International Mobile Equipment Number (IMEI). The IMEI can be found by typing *#06# into the handset and should be written down and stored securely.
Protecting business vehicles and transported goods
Any vehicles you own should be treated in the same manner as the shell of your business. You should always secure the doors and windows and have a lockable box in the cargo area. You can also add extra security, such as:
- an alarm
- a vehicle tracking system
- an immobiliser
- a steering lock
For high-value vehicles and machinery, such as tractors or plant machinery, you could consider marking property or fitting a tracking device. Read PSNI guidance to help prevent plant machinery thefts.
Reflective film on the windows will help to hide the interior. You should always make sure that anything left inside is hidden from view and use signs to let people know that nothing of value is left inside. If your business receives a lot of cash over the counter, it should be removed frequently to a secure location.
Secure lorry parks should be used for overnight stops.
For goods delivered by post, it might be appropriate to use a more secure service such as recorded or special delivery.
Building site security
Building sites are often the target of crime with a lot of high-value plant, machinery, and tools on site along with large quantities of materials such as cement, bricks, concrete blocks, steel, and timber. See the National Business Crime Centre's guidance on construction site security.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/secure-your-business-assets
Links
Business security: cash
How to handle cash, cheques, and debit and credit card payments securely.
If you or your employees handle cash, try to avoid getting into a routine when depositing it to a bank or building society. It is also wise to reduce the amount of cash held on your business premises where possible. This can be done by:
- making a regular, secure payment into the bank
- transferring excess cash into a locked tamper-proof unit
- removing cash overnight - eg emptying tills
- encouraging the use of electronic payments, credit/debit cards or cheques
- paying wages straight into staff bank accounts
Keeping cash on site
If cash has to be kept on-site, you should make sure it is held in a secure manner - eg a safe that is fitted to the building. Where possible the minimum amount of cash should be held in public areas and tills should be cleared regularly. Drop-safes, with time-locking mechanisms, should be used to ensure that cash is held securely.
Staff should not handle cash alone and anyone who deals with financial records should not handle cash.
Moving cash around
When you or an employee makes a secure payment to the bank, it should not be made alone. It is also advisable to vary the times and the route used. Restrict information about cash movement to those directly involved and consider using a professional cash-in-transit business.
Stained and counterfeit cash
Encourage your staff to be aware of the risk of accepting stained notes as these could have been stolen. Notes become stained when a cash degradation system has been set off during a robbery. These systems are used in tills (by banks, post offices, building societies, and retail outlets), cash points, and cash boxes used by cash-in-transit companies that deliver and collect cash.
If you are offered a stained note by a member of the public, treat it as you would a mutilated or damaged note and do not accept it. Advise the customer to take the note to a Post Office or bank and obtain a Bank of England Mutilated Note (BMN) claim form for the repayment of damaged notes see further information on damaged and contaminated banknotes. By filling in this form and going through the proper channels, providing the note is genuine, they will be reimbursed for the note they have handed in.
There are a number of ways to tell if a note is counterfeit or genuine. It is illegal to keep or pass on fake notes. Stopping criminals from spending stained or counterfeit notes helps to remove the incentive for crime.
Cheques
The number of cheques being used has declined in preference to the use of online banking and electronic payment systems. These systems have the benefit of additional security and anti-fraud measures. In spite of this cheque, fraud has become more organised and sophisticated with advances in computer and printing technology.
Writing cheques
When writing cheques:
- always fill out cheques with the full details of the payee
- avoid any blank spaces and rule out any unused space
- when sending by post, it is best to send securely and not use a windowed envelope
- store cheques securely and use them in serial number order
- be sure to compare cheques written with the correct paperwork
- destroy spoiled cheques by shredding if possible
Accepting cheques as payment
When accepting cheques:
- ensure they are written, signed, and torn out in front of you
- check that date and amount are correct
- don't release goods before bank drafts are cleared
- if you receive a cheque for far too much and are asked to send the balance back to the drawer by electronic funds transfer, this is probably a scam where the cheque will bounce but your account is still debited
Debit or credit cards
You must have procedures in place for handling credit and debit cards. The secure chip and pin system should be used where possible. If you are unable to use chip and pin, you should check the cards for:
- start and expiry dates
- signs of tampering
- matching number on the card and till printout
- matching signature
If in doubt, you can always phone the card issuer for authorisation.
Contactless payment has become a more popular method of paying through cards as well as wearable and mobile devices.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/business-security-cash
Links
Business security: stock and theft prevention
Keep track of stock, maintain security, and avoid staff theft by restricting access to stock and using CCTV.
Keeping stock secure depends on knowing what you have and where it is located, so you should keep records of when stock is sold, used, replaced, or thrown away. In order to keep stock secure, you should:
- keep records of stock with regular stock checks - including deliveries
- stock control system - ensure a system of reporting stock variations is in place and amendments to the records only take place after authorisation, see stock control systems - keeping track using computer software
- keep stock away from doors and in a place where it takes an obvious action to reach
- use secure lockable, fireproof cabinets or rooms for high-value stock
- use mirrors or closed-circuit television (CCTV) to keep stock and equipment monitored
- try to limit the number of people who have access to valuable stock
Thieves and shoplifters
Staff should always be vigilant for any suspicious behaviour and should take appropriate action, such as reporting an incident. Suspicious behaviour could include:
- choosing purchases quickly
- trying to rush the transaction
- working in groups to distract your staff
- splitting purchases between different debit or credit cards
To find out what else you can do to deter this type of crime, see top tips to reduce shoplifting.
Prevent theft by staff
There are a number of measures you can take to combat theft by staff, for example:
- create an honest work culture - educate your staff about the potential costs of theft and have a clear, communicated policy on this issue
- restrict access to warehouses, stockrooms, and stationery cupboards
- install CCTV in staff car parks
- regularly change staff who control stock to avoid collusion or bad practice
Staff credentials
Before you employ a new staff member, you should check the identity of the staff member and their references thoroughly.
You are also required to check that potential employees have the right to work in the UK. See pre-employment checks.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/business-security-stock-and-theft-prevention
Links
Reporting a crime against your business
How to report a crime against your business to the PSNI or Crimestoppers.
If you need to report a crime against your business in an emergency dial 999.
Non-emergencies
For non-emergency incidents and general enquiries, dial 101 - the Police Service of Northern Ireland's (PSNI) non-emergency number. A trained member of staff will take your call. Contact the PSNI.
When you ring the police to report a crime, the police will give you a Crime Index number. Keep this number for future reference, as you might need it when discussing the incident or accessing police records.
Anonymously report a crime
You can also report crime anonymously by calling Crimestoppers, an independent charity helping law enforcement locate criminals and help solve crimes. You can call Crimestoppers on Tel 0800 555 111.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/reporting-crime-against-your-business
Links
Preventing identity theft, scams and fraud
How to protect your business from the risk of identity theft.
Identity theft and fraud can be a threat to your business, particularly if you carry out any part of your business online.
The target of fraud may be an individual within the business or the business itself. Criminals use a wide range of methods and approaches to commit their crimes. The aim is usually to steal sufficient information to assume the identity of the person or business with the aim of obtaining goods, services, or credit fraudulently.
One of the most common methods of stealing your corporate identity is through your IT system. Fraudsters may use 'malware' to access usernames, passwords, or bank details - detect spam, malware, and virus attacks.
Another method is the use of phishing websites which use keystroke logging software to record your keyboard strokes as a way of stealing financial details. Protect your business against phishing.
Protect your business from scams
There are many forms of scams designed specifically to target businesses. You should familiarise yourself and your staff with key signs of a scam. See PSNI guidance to protect yourself from scams and fraud.
You can protect your business from scams in several ways. For example, you should:
- Limit the number of employees authorised to approve purchases of goods and services, and ensure that all other employees know they cannot discuss ordering or payments.
- Never agree to anything in a rush. Remember, it is possible to make a legally binding contract over the phone, and the main problem with oral contracts is proving exactly what was said and agreed. Generally, it is one person's word against another's.
- Do some research on the goods or service being offered.
- Read the small print thoroughly before signing any paperwork, so that you know what you are committing to and how much it might cost.
- Keep copies of all paperwork, proof of postage and all other correspondence.
Don't be pressured into paying for services you have not agreed to, that don't match what you ordered, or that were promised and haven't been provided. You should take advice on your legal rights if you are unsure.
If you are threatened with debt collectors or a credit 'black listing', remember that only a court can decide whether you are liable to pay, and disputes with another business will not necessarily affect your credit rating.
See the Little Book of Big Scams for further guidance on how to protect your business from scams.
Telephone preference service
If you are a sole trader or a partnership you can register with the Telephone Preference Service (TPS) by calling the TPS Registration Helpline on Tel 0345 070 0707.
The TPS is a central opt-out register, whereby individuals can register their wish not to receive unsolicited sales and marketing telephone calls. It is a legal requirement that businesses do not make such calls to numbers registered on the TPS.
Minimise the risk of identity theft and fraud
To prevent IT fraud your business should implement anti-virus software and firewalls. You should also introduce internet and email policies to reduce the risk of employees inadvertently disclosing sensitive information. See how to protect your business online.
Another scam involves fraudsters stealing your entire corporate identity. Fraudsters attempt to do this by changing the information your business has registered with Companies House. Find out how you can protect your company from corporate identity theft.
You can help prevent identity fraud through the secure destruction of sensitive business information. When you need to destroy information in paper or electronic formats, make sure that you use reputable suppliers that comply with European standards, particularly EN 15713.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/preventing-identity-theft-scams-and-fraud
Links
Business security plans and procedures
Plans and procedures to physically secure your business property and assets.
Your business should have adequate security and safety procedures and staff should be made aware of them. This could be anything from a simple procedure like locking a delivery door immediately after deliveries, or a more complex procedure like using security staff or an alarm system.
Locking up after close of business
You should also have a set procedure for securing your business premises. This should involve checking that all doors and windows are locked, lights and computers are switched off and the alarm and any other security measures are switched on. Pay special attention to areas where you store combustible materials or rubbish. Regularly test fire and smoke detectors to make sure they work.
You should consider a security plan to protect both equipment and information, such as:
- removing equipment from a vehicle overnight
- storing equipment securely
- locking the equipment room
- encouraging staff to be vigilant
Using signs as a security measure
A well-placed sign can help put off a criminal. For example, you could use signs stating:
- all properties are marked and easy to identify
- no cash is held on the premises
- staff have no access to the safe
- all tools removed from this vehicle
- closed-circuit television (CCTV) in operation
- no stock left overnight
All employees should be aware of their security duties and you should check that your security measures are followed.
When necessary, employees should dial 999 or get help quickly by using an alarm. They should also try to write down information about the incident and secure CCTV footage and the scene until the police arrive.
For more information, see business continuity and crisis management.
ActionsAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/business-security-plans-and-procedures
Links
CCTV surveillance
Choose an appropriate closed-circuit television system to deter intruders and potentially lower insurance premiums.
Closed-circuit television (CCTV) uses cameras to monitor the inside and/or outside of your premises. Some CCTV systems require manual operation, either by a private monitoring company or an appropriate member of staff.
Benefits of CCTV
CCTV can help by:
- deterring thieves
- watching remote areas or more than one area at once
- enabling premises to be watched in safety
- helping police to identify and prosecute intruders
Choosing a CCTV system
Your choice of CCTV system will depend on the value of your stock, machinery, or office equipment and the type and location of your premises.
Ask your insurance company or crime prevention officer for advice. You can find an approved security supplier.
Placing the cameras
Position cameras in areas:
- particularly vulnerable to intruders
- where staff could be alone or at risk, such as car parks
- hidden from view or which are particularly quiet
You should put up a notice stating that you have a CCTV system. Cameras need to be easy to spot to have a deterrent effect. You can use dummy cameras as a cheap deterrent, either on their own or to make a real CCTV system look bigger. However, relying heavily on these is risky because potential thieves might realise they are fake. Try to:
- protect cameras from attack
- avoid blocking camera views with high-sided vans, trees, etc
- adopt a tape archive system that can be used as evidence if necessary
Make sure that the system is correctly set up and that tapes are capable of recording images clearly. If the system is not recording images sufficiently it may be difficult to identify the perpetrators.
Insurance requirements
Your insurers may specify the kind of system they want you to install. They may also want your system and installer to be inspected by the National Security Inspectorate (NSI) or SSAIB.
CCTV and data protection
If your business uses closed-circuit television (CCTV), you have a legal duty under the Data Protection Act to make sure that individuals' rights are protected. You usually have to register with the Information Commissioner's Office (ICO) if your business operates CCTV. Failure to do may be a criminal offence and you could face a fine. See if you need to register with the ICO.
CCTV operators must follow the correct procedures when they gather, store, and handle images:
- You must tell people that they may be recorded by CCTV, eg by displaying signs. These must be clearly visible and readable. See the ICO's guidance on the right to be informed.
- Individuals have the right to request images that you have recorded of them. You must provide these within one calendar month. See the ICO's guidance on the right of access to personal data.
- Release of CCTV images must be controlled and in line with the system's intended purpose. For example, if the system is intended to help prevent and detect crime, you can disclose images to law enforcement agencies.
- You should only keep recorded images for as long as needed. See the ICO's guidance on data storage limitation.
See the ICO's CCTV checklist. Read further guidance on the UK General Data Protection Regulation (UK GDPR).
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/cctv-surveillance
Links
Registering as a landlord
Tenancy Deposit Scheme
Landlords are required to protect the tenant's deposit in a scheme.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
If you are a landlord or letting agent in Northern Ireland and take a deposit on a private tenancy on or after 1 April 2013, then you are required to protect the deposit within 28 calendar days of receiving it using either an insurance or custodial-based protection scheme.
From 1 April 2023, you must not ask for or retain a deposit that is more than one month's rent.
You must also provide certain information about which Tenancy Deposit Scheme is protecting it and you must serve this on your tenants within 35 calendar days of receiving the deposit - this is called 'Prescribed Information'.
Three organisations have been appointed by the Northern Ireland Executive to administer the scheme and further information can be found on each of their websites:
Guidance for tenants
Tenants can read full details of how the Tenancy Deposit Scheme works.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/tenancy-deposit-scheme
Links
Registering as a landlord
All landlords in Northern Ireland must register for the Landlord Registration Scheme.
Landlord Registration Scheme
The Landlord Registration Scheme collects and maintains up-to-date and accurate information on landlords and their properties. All landlords with properties in Northern Ireland must be registered with the scheme. The registration lasts for three years.
Who has to register?
All landlords who let properties under private tenancy in Northern Ireland must register for the Landlord Registration Scheme. You must provide accurate and up-to-date information about yourself and your properties. All joint owners of a property that is let need to register separately.
Renewing your registration
The landlord registration certificate is valid for three years after which you must renew your landlord registration.
Register as a landlord or renew your landlord registration.
How much does it cost?
You only pay one fee regardless of the number of properties you own:
- the online registration fee is £70
- the paper/non-electronic based registration fee is £80
Who is exempt from the registration fee?
As a landlord, you are exempt from the registration fee if you have paid to register a house in multiple occupation which is registered under a Houses in Multiple Occupation Registration Scheme.
Penalties
If you do not complete your registration, you will be committing an offence and may be issued with a penalty of between £500 and £2,500.
Read further information on the registering as a landlord.
Information for landlords who use agents
If someone else looks after the day to day management of your property or if the house is sub-let, you, as the landlord, will still have responsibility for and control of the property. Your property will still have to be registered under the Landlord Registration Scheme.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/registering-landlord
Links
Register a house in multiple occupation
Houses rented to 3 or more unrelated people must be registered as an HMO.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
If you rent out a property to 3 or more unrelated people who share the bathroom or toilet and kitchen, you must register it as a house in multiple occupation (HMO). An HMO, also known as a house share, must meet certain requirements and be registered with your local council.
Houses in Multiple Occupation.
Your responsibilities as a landlord
As a landlord of an HMO, you must:
- ensure the property is not overcrowded
- make sure the property is fit for multiple occupants, ie there is enough cooking space and washing facilities
- provide your local council with all the necessary information about your HMO
Fees for HMOs
You'll have to pay a fee for registration and for any future renewals. Registration is usually valid for 5 years, after this time you can make a renewal. The cost is based on the number of occupants at the property; the more occupants there are, the higher the fee will be. HMO advice for landlords.
How to register your HMO
You can register your HMO by contacting your local council. Find contact details of local councils in Northern Ireland.
Fines and penalties
If you breach any of your agreements with your local council, it may result in a fine, including:
- up to £1,000 for failing to provide the information requested
- up to £5,000 for providing false information
- up to £2,500 if found guilty of overcrowding
- up to £5,000 if someone is living in a part of the property that is deemed unfit for occupation (you'll then be charged up to 10% of the fine every day this continues)
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/register-house-multiple-occupation
Links
Certificate of fitness for rental properties
To rent out a property, you must obtain a certificate of fitness from your local council.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
If you want to rent out a property, you may have to apply to your local council for a certificate of fitness. The certificate of fitness shows that a house is suitable for human habitation and allows you to charge rent at market price.
Applying for a certificate of fitness
Contact the Environmental Health Department of your local council to request a fitness inspection. Find local council contact details in Northern Ireland.
A fee of £50 will be charged for the initial inspection. You will have to complete an application form, providing certain information about your property, including when it was built, the number of rooms, and the facilities provided. This fee will not be refunded if it turns out your property does not require a certificate of fitness, so be sure to check your property's particulars against the exemptions above.
The property inspection
The Environmental Health Officer (EHO) who carries out the inspection will assess the property to ensure that it meets the fitness standard and is fit for human habitation. If the property passes the inspection you will receive a certificate of fitness and be free to charge tenants at a market rate.
If your property fails the inspection, you will receive a schedule of work that will bring the property up to standard. Until this work is completed and the property is re-inspected (for a £100 fee), it will become rent-controlled and the Rent Officer for Northern Ireland will restrict how much rent you are allowed to charge.
Who is exempt?
You don't need to apply for a certificate of fitness if:
- the tenancy began before 1 April 2007
- a renovation or houses in multiple occupation (HMO) grant has been paid by the Northern Ireland Housing Executive (NIHE) (this only applies for a period of ten years from the date of the grant)
- the property is registered with NIHE as an HMO, see register a house in multiple occupation
- the property was formerly let under a protected or statutory tenancy where a regulated rent certificate has been issued (this only applies for a period of ten years from the date of issue of the certificate)
Fines and penalties
If you fail to apply for the inspection of a qualifying property within 28 days of a new tenancy being granted, you may be fined up to £2,500.
Content category
Source URL
/content/certificate-fitness-rental-properties
Links
Rental property health and safety
Landlords' health and safety responsibilities when letting property.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
As a landlord, you are responsible for ensuring the safety of your property. Aside from the general requirements needed for a certificate of fitness for rental properties, you must also meet the following safety requirements.
Electrical safety in rental properties
All mains electrical equipment, new or second-hand, that you supply with the accommodation must be safe and adequate for the needs of your tenant. You must meet the requirements of regulations for supplying electrical equipment. Most equipment with CE marking will satisfy the requirement, as long as they remain in good working order.
Electrical safety: advice for landlords.
Furniture safety in rental properties
If you are providing furnished accommodation, all furniture you supply must comply with fire safety regulations. Many domestic fires start with soft furnishings and toxic fumes given off when upholstery material burns can be fatal; regulations exist to reduce this risk.
Gas safety in rental properties
If your property has gas heating or any gas appliances, you are legally required to have the boiler and any gas appliances inspected every year.
The inspection must be carried out by a Gas Safe registered engineer. Gas safety information for landlords.
Carbon Monoxide has no smell, taste or colour, but it is extremely dangerous and can be fatal. If you install a new or replacement fuel-burning appliance, whether it is gas, coal or oil fired you are legally required to install a carbon monoxide detector in the room where the appliance is located.
Fire alarms in rental properties
If you're building a new property to rent out, or converting a new property you'll have to install fire alarms to comply with building regulations. If your property has three or more non-related tenants (an HMO) you are legally required to install a fire alarm. There is no legal requirement for non-HMO properties, however, landlords should install fire alarms to protect any tenants living there. Failing to install a fire alarm could invalidate your insurance policy. Fire safety advice.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/rental-property-health-and-safety
Links
Landlords’ responsibilities
Rules that landlords must follow when letting out property and their obligations to tenants.
The law on private renting in Northern Ireland changed on 1 April 2023. For further details read the Private Tenancies Act (Northern Ireland) 2022.
As a landlord, there are some rules you must follow and certain obligations you have to your tenants.
Requirements for smoke, heat and carbon monoxide alarms
New regulations were introduced on Thursday 30 May 2024 to set a minimum standard for smoke, heat and carbon monoxide alarms in private rental properties.
Landlords' responsibilities for alarm units
It is the responsibility of the landlord to:
- install and keep in proper working order sufficient alarms for detecting smoke, heat and carbon monoxide within any property that they rent out to tenants
- repair or replace any alarm that they have been informed of that is faulty
- ensure that any alarm units (smoke, heat & carbon monoxide) that are bought/installed are marked/referenced as being British Standard compliant
- ensure that if any alarms are to be hardwired into the main electrical installation, that work is undertaken by a qualified electrician
- confirm the tenant is satisfied all alarms are in working order on the commencement of any tenancy
- advise tenants that they need to regularly test the alarms according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and to report any faults to the landlord
Read full details on landlords' responsibilities for alarm units in private rental properties.
Compliance dates
Existing tenancies granted before Sunday 1 September 2024 must comply by Sunday 1 December 2024. New tenancies granted on or after Sunday 1 September 2024 must be compliant on the date the new tenancy is granted.
Repairs in rental properties
In the day-to-day maintenance of the property, you are responsible for any repairs to the structure of the property and any furnishings or equipment supplied with the property. The tenant is responsible for any repairs to their belongings or damage that is their fault.
Records landlords must keep
You are obliged to keep the following records:
- a gas safety certificate, for any gas appliances on the property
- an Energy Performance Certificate
- information on the tenancy deposit protection scheme you've chosen to protect the tenant's deposit and some prescribed information relating to the deposit
- an inventory
You are advised to keep the following records:
- a copy of the Tenancy Information Notice supplied to your tenant(s)
- copies of any receipts for cash payments made by your tenant(s)
Communication with tenants
If you are planning any action that will impact your tenants, you should inform them in a timely manner. Let your tenants know in advance of any of the following:
- repairs and improvements to the property
- sale of the property/the property being repossessed
- you or anyone else entering the property (normally you will need the tenant's permission)
It is important that your tenants are able to contact you when a problem arises and that you respond within a reasonable time. Even if your property is managed by an agent, you still must give your name, a correspondence address, and telephone to the tenant in the Tenancy Information Notice.
Deposits for private rental properties
If you take a tenancy deposit for a private tenancy on or after 1 April 2013 you are legally obliged to protect this deposit in an approved scheme. If the deposit was taken before 1 April 2013 it does not need to be placed in a protection scheme, but you should keep it in a separate account, have clear records about when you received the deposit, and give your tenants a receipt. Read more about the Tenancy Deposit Scheme.
From 1 April 2023, you cannot ask for or retain a tenancy deposit of more than one month's rent. See further information on changes to tenancy deposits.
Also on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/landlords-responsibilities
Links
How Land & Property Services uses your information
Business rates and types of premises
Types of property that must pay business rates and those that are excluded.
Business or non-domestic premises include most commercial properties, such as shops, offices, pubs, warehouses, and factories.
Properties excluded from the valuation list for business rates
However, there are some types of properties that are specifically excluded from the valuation list and therefore not subject to rates:
- fish farms
- most farmland and farm buildings
- most cemeteries and crematoriums
- turbary and fishing rights
- moveable moorings
- public parks
- sewers
Properties exempt or partially exempt from business rates
Some other non-domestic premises that are exempt or partially exempt from rates include:
- places of public religious worship and church halls
- district council swimming pools and recreation facilities
- charity shops selling only donated goods
- ATMs in designated rural wards
Mixed-use properties and business rates
If part of a building is used for business and part for residential purposes - such as a shop with a flat above or a solicitor's office in a domestic property - the part used for business counts as non-domestic premises. So, if you live and work on the same premises, you generally pay business rates on the part of the property used for business and domestic rates on the residential part.
Rental properties and business rates
Special rules apply to landlords, owners, and tenants depending on the level of Capital Value for domestic properties or Net Annual Value for non-domestic properties. Rental properties and business rates.
Working from home and business rates
If you use your home as a workplace, the part of the property used for work may be liable for business rates. You will still have to pay domestic rates on the rest of the property. Whether you are charged business rates or not depends on the degree of business use. You are more likely to have to pay business rates if a room is used exclusively for business or has been modified, eg as a workshop. Each case is considered individually.
Queries on your business rates
If you have a query regarding your business rates you should contact Land & Property Services.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/business-rates-and-types-premises
Links
How business rates are calculated
How rates are calculated for business premises and how to get an idea of what your rate bill may be.
Your rate bill is made up of a number of parts including the regional rate, the district rate and Net Annual Value (NAV). Your rate bill is calculated by multiplying the NAV of your property by the non-domestic rate poundage (non-domestic regional rate + non-domestic district rate) for your council area for the relevant year (as shown below):
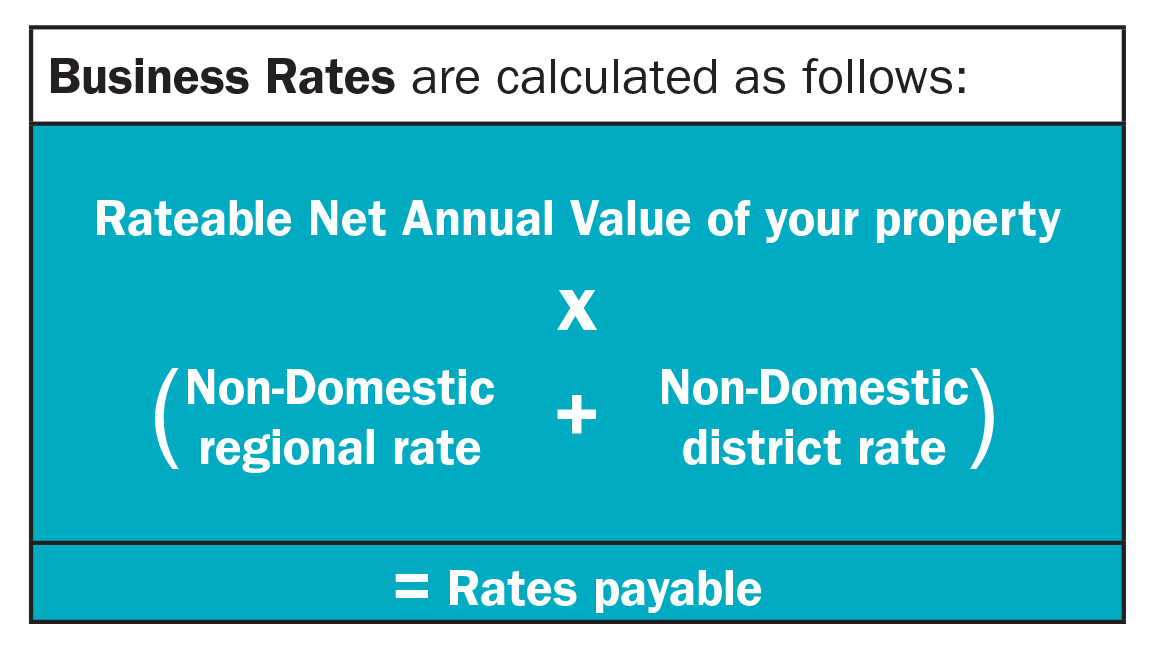
Regional and district rates
The regional rate is set annually by the Northern Ireland Executive and is applied to each district council area in Northern Ireland. The district rate is set annually by each district council in Northern Ireland.
Find the the 2024-25 non-domestic rate poundages for your council area.
Net Annual Value
Rates for non-domestic or business properties are assessed on their rental value, also known as the Net Annual Value (NAV). NAV is an assessment of the annual rental value that your property could reasonably be expected to be let for if it was on the open market. Each non-domestic property is valued in line with comparable properties in the vicinity.
The current valuation list for non-domestic properties came into operation on 1 April 2023 and is based on rental values as at 1 October 2021.
Find a property valuation for your business premises.
View your estimated rate bill
You can view an estimate of a full annual rate bill for the current rating year by inputting the address information using the LPS online valuation search.
Find a property valuation and view your estimated rate bill.
Queries on your business rates
If you have a query regarding business rates or are unsure of your outstanding bill you should contact Land & Property Services.
Reval 2026
The short video below explains the latest revaluation process, known as Reval 2026, which will create a new valuation list that will be used to calculate business rate bills from April 2026.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/how-business-rates-are-calculated
Links
Rates for retail units
How business rates are calculated for retail units and how this differs from other types of non-domestic properties.
When calculating business rates for retail units Land & Property Services (LPS) assess the Net Annual Value (NAV) by using zoning. Zoning is a methodology used in assessing the rental value of retail units and is used for shops, hair salons, banks, betting shops and most restaurants. LPS use zoning as it helps take into account different sizes and shapes of shops and awkward layouts.
LPS also consider other parts of the property that are ancillary or tertiary spaces such as upstairs offices and store rooms. They are rated but zoning is not applied for these areas of the property. Some spaces are not considered useable retail areas and are excluded from valuation. These spaces include toilets, lobbies, plant rooms and stairwells.
Queries on your business rates
If you have a query regarding business rates you should contact Land & Property Services.
Reval 2026
The short video below explains the latest revaluation process, known as Reval 2026, which will create a new valuation list that will be used to calculate business rate bills from April 2026.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/rates-retail-units
Links
Rates for licensed premises
How business rates are calculated for licensed premises and how this differs from other types of non-domestic properties.
When calculating business rates for licensed premises Land & Property Services (LPS) assess the Net Annual Value (NAV) by calculating the correct level of Fair Maintainable Trade (FMT). LPS does this by collecting information about rent, trading receipts, and trading patterns. LPS analyse this information along with the type of premises, the area it is in, and what services it offers.
As there is little evidence of rents for pubs LPS uses FMT in the assessment to help assess a rateable value or NAV. This is the industry standard and is the approach adopted across the UK.
LPS applies a percentage to the estimated FMT to assess the annual rent. It is based on factors such as, where the premises are located, the sort of premises they are (bar, hotel, etc.), and the sort of trade carried on. LPS regularly consults with trade associations to ensure its approach continues to reflect how the licensed industry operates.
Reval 2026
The short video below explains the latest revaluation process, known as Reval 2026, which will create a new valuation list that will be used to calculate business rate bills from April 2026.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/rates-licensed-premises
Links
Business rates: occupying and leaving a property
How your business rates are affected if you occupy or leave a property and how to inform Land and Property Services of changes.
Moving into a new business property
When you move into your new property, you must contact your regional Land & Property Services (LPS) Rating office to let them know, otherwise you may receive a backdated rate bill. You can also advise them of how you wish to pay your rate bill.
Moving into a newly built business property
If you are moving into newly built premises you should contact your local LPS Valuation office. A valuer will come out to assess your property. A rate bill will then be issued based on this valuation. You should be aware that failure to inform LPS could lead to the issue of a backdated rate bill.
You can apply online to have your new property valuation assessed or alternatively you can download the LPS application form (CR3) to have your property valued (PDF, 230K).
This is a writable document, which means that you can complete on screen, print and send to LPS. Alternatively, you can save the document to your desktop, complete the form and send as an attachment to your local LPS Valuation office.
Leaving your old business property
When you move out of your property you must contact LPS. You should have your Account ID, Ratepayer ID and details of the new owners or people in your property to hand.
Alternatively you can use the online form to make changes to your rate account such as personal information, billing address for your rate bill, notification of a ratepayer's death or to change the assessment period for your rate account.
Queries on your business rates
If you have a query regarding business rates you should contact Land & Property Services.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/business-rates-occupying-and-leaving-property
Links
How Land & Property Services uses your information
How LPS uses customer data and how they protect this data under the legislation.
Land & Property Services (LPS) fully complies with the Data Protection Act 2018 and the Department of Finance's Data Protection Policy. This means that how LPS collect, store, use, and disclose/share the information you provide to them meets the standards of this legislation.
Reasons why LPS collates and holds customer information
- For the purpose of billing
- Collection and recovery of rate revenue
- Assessment of benefit/relief claims
- The creation and maintenance of Valuation Lists
- The Land Registration Public Register
LPS and the National Fraud Initiative
LPS has a duty to protect public funds and to this end may use the information provided for the prevention and detection of fraud.
LPS participates in the National Fraud Initiative, an exercise that matches electronic data within and between audited bodies to prevent and detect fraud.
The use of data by the Audit Commission does not require the consent of the individuals concerned under the Data Protection Act 2018. However, it is controlled to ensure compliance with data protection and human rights legislation.
For more information contact LPS or Tel 0300 200 7801.
Developed withAlso on this siteContent category
Source URL
/content/how-land-property-services-uses-your-information
Links